Seroprevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus infection among blood donors in China: a first nationwide survey
- PMID: 33413457
- PMCID: PMC7791705
- DOI: 10.1186/s12977-020-00546-w
Seroprevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus infection among blood donors in China: a first nationwide survey
Abstract
Background: So far, the prevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) type 1 and 2 in some highly populated countries such as China is still unknown. In this study, a multi-center nationwide serological survey was designed and performed, to reveal the seroprevalence of HTLV infection among Chinese blood donors.
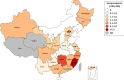
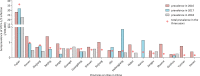
Results: Among 8,411,469 blood donors from 155 blood establishments, 435 were finally confirmed as HTLV carriers. The prevalence of HTLV infection in China varied in different provinces: Fujian had the highest prevalence of 36.240/100,000 (95% CI 31.990-41.050) and eleven provinces did not find HTLV-seropositive donors in the three years. no HTLV-2 infection was found. The overall prevalence of HTLV-1 in China decreased from 2016 to 2018. Female was identified as an independent risk factor of HTLV infection in China. Besides, seroconversion was observed in two of seven seroindeterminate donors 85 and 250 days after their last donation, respectively.
Conclusions: The seroprevalence of HTLV infection in most areas of China among blood donors is quite low, but it varies significantly in different geographic areas. Screening anti-HTLV-1/2 antibody and follow-up of serointederminate donors are essential to ensure blood safety especially in areas where we have found HTLV infected donors.
Keywords: Blood donor; Human T-lymphotropic virus; Seroprevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I and II seroprevalence among volunteer blood donors in Thailand.Pathog Glob Health. 2018 Oct;112(7):343-348. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2018.1541576. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Pathog Glob Health. 2018. PMID: 30424716 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus-1/2 in Blood Donors in Northern Pakistan: Implications for Blood Donor Screening.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015 Dec;25(12):874-7. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015. PMID: 26691361
-
Human T lymphotropic virus types I and II proviral sequences in Argentinian blood donors with indeterminate Western blot patterns.J Med Virol. 2004 Oct;74(2):323-7. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20172. J Med Virol. 2004. PMID: 15332282
-
The prevalence and significance of HTLV-I/II seroindeterminate Western blot patterns.Viruses. 2011 Aug;3(8):1320-31. doi: 10.3390/v3081320. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
History and update of HTLV infection in China.Virus Res. 2014 Oct 13;191:134-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.07.036. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 25109546 Review.
Cited by
-
Limitations of human t-lymphotropic virus type 1 antibody testing in hospitals of endemic regions in China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Apr 3;15:1474526. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1474526. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40248369 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic typing and intrafamilial transmission of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 in non-endemic areas of China.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 18;14:1288990. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1288990. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37920260 Free PMC article.
-
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (SWOT) Analysis of the Implementation of Public Health Policies on HTLV-1 in Brazil.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 7;9:859115. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.859115. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35462992 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter cross-sectional study of HTLV-1 prevalence and associated risk factors in epidemiologically relevant groups across Brazil.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 3;13:1511374. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1511374. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40098798 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a duplex real-time PCR for the rapid detection and quantitation of HTLV-1.Virol J. 2023 Jan 17;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-01970-y. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 36650537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoshida M, Seiki M, Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984;81:2534–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

