Essential amino acid-enriched whey enhances post-exercise whole-body protein balance during energy deficit more than iso-nitrogenous whey or a mixed-macronutrient meal: a randomized, crossover study
- PMID: 33413462
- PMCID: PMC7791816
- DOI: 10.1186/s12970-020-00401-5
Essential amino acid-enriched whey enhances post-exercise whole-body protein balance during energy deficit more than iso-nitrogenous whey or a mixed-macronutrient meal: a randomized, crossover study
Abstract
Background: The effects of ingesting varying essential amino acid (EAA)/protein-containing food formats on protein kinetics during energy deficit are undetermined. Therefore, recommendations for EAA/protein food formats necessary to optimize both whole-body protein balance and muscle protein synthesis (MPS) during energy deficit are unknown. We measured protein kinetics after consuming iso-nitrogenous amounts of free-form essential amino acid-enriched whey (EAA + W; 34.7 g protein, 24 g EAA sourced from whey and free-form EAA), whey (WHEY; 34.7 g protein, 18.7 g EAA), or a mixed-macronutrient meal (MEAL; 34.7 g protein, 11.4 g EAA) after exercise during short-term energy deficit.
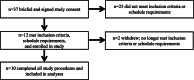
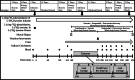
Methods: Ten adults (mean ± SD; 21 ± 4 y; 25.7 ± 1.7 kg/m2) completed a randomized, double-blind crossover study consisting of three, 5 d energy-deficit periods (- 30 ± 3% of total energy requirements), separated by 14 d. Whole-body protein synthesis (PS), breakdown (PB), and net balance (NET) were determined at rest and in response to combination exercise consisting of load carriage treadmill walking, deadlifts, and box step-ups at the end of each energy deficit using L-[2H5]-phenylalanine and L-[2H2]-tyrosine infusions. Treatments were ingested immediately post-exercise. Mixed-muscle protein synthesis (mixed-MPS) was measured during exercise through recovery.
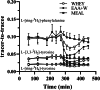
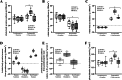
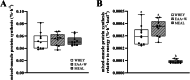
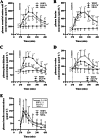
Results: Change (Δ postabsorptive + exercise to postprandial + recovery [mean treatment difference (95%CI)]) in whole-body (g/180 min) PS was 15.8 (9.8, 21.9; P = 0.001) and 19.4 (14.8, 24.0; P = 0.001) greater for EAA + W than WHEY and MEAL, respectively, with no difference between WHEY and MEAL. ΔPB was - 6.3 (- 11.5, - 1.18; P = 0.02) greater for EAA + W than WHEY and - 7.7 (- 11.9, - 3.6; P = 0.002) greater for MEAL than WHEY, with no difference between EAA + W and MEAL. ΔNET was 22.1 (20.5, 23.8; P = 0.001) and 18.0 (16.5, 19.5; P = 0.00) greater for EAA + W than WHEY and MEAL, respectively, while ΔNET was 4.2 (2.7, 5.6; P = 0.001) greater for MEAL than WHEY. Mixed-MPS did not differ between treatments.
Conclusions: While mixed-MPS was similar across treatments, combining free-form EAA with whey promotes greater whole-body net protein balance during energy deficit compared to iso-nitrogenous amounts of whey or a mixed-macronutrient meal.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, Identifier no. NCT04004715 . Retrospectively registered 28 June 2019, first enrollment 6 June 2019.
Keywords: And energy restriction; Free-form amino acids; Muscle protein synthesis; Whole-body protein turnover.
Conflict of interest statement
JAG, DDC, AHM, JTA, MAW, ANV, CTC, NEM, LMM, JWC, AAF, and SMP have no conflicts of interest associated with this research. RRW is an inventor of patent entitled “Composition for Stimulating Muscle Growth, Repair, and Maintenance,” US Patent (16; 382,984). RRW is a shareholder in Essential Blends, LLC, and The Amino Company, LLC. RRW was not involved in data collection or analyses and was blinded to all data until final consolidation into manuscript form by JAG and SMP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of high versus standard essential amino acid intakes on whole-body protein turnover and mixed muscle protein synthesis during energy deficit: A randomized, crossover study.Clin Nutr. 2021 Mar;40(3):767-777. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.07.019. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32768315 Clinical Trial.
-
Consuming Whey Protein with Added Essential Amino Acids, Not Carbohydrate, Maintains Postexercise Anabolism While Underfed.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2025 Jan 1;57(1):70-80. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000003541. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2025. PMID: 39160756 Clinical Trial.
-
Muscle Protein Synthesis and Whole-Body Protein Turnover Responses to Ingesting Essential Amino Acids, Intact Protein, and Protein-Containing Mixed Meals with Considerations for Energy Deficit.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 15;12(8):2457. doi: 10.3390/nu12082457. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32824200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anabolic response to essential amino acid plus whey protein composition is greater than whey protein alone in young healthy adults.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020 Feb 10;17(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-0340-5. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32041644 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
International society of sports nutrition position stand: nutrient timing.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017 Aug 29;14:33. doi: 10.1186/s12970-017-0189-4. eCollection 2017. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017. PMID: 28919842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
International society of sports nutrition position stand: tactical athlete nutrition.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2022 Jun 23;19(1):267-315. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2022.2086017. eCollection 2022. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35813846 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in nutritional metabolic therapy to impede the progression of critical illness.Front Nutr. 2024 Jul 5;11:1416910. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1416910. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39036495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconsidering the pre-eminence of dietary leucine and plasma leucinemia for predicting the stimulation of postprandial muscle protein synthesis rates.Am J Clin Nutr. 2024 Jul;120(1):7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.04.032. Epub 2024 May 3. Am J Clin Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38705358 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Supplementation and Exercise as Essential Allies in the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure: The Metabolic and Molecular Bases.Nutrients. 2023 May 16;15(10):2337. doi: 10.3390/nu15102337. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meals Containing Equivalent Total Protein from Foods Providing Complete, Complementary, or Incomplete Essential Amino Acid Profiles do not Differentially Affect 24-h Skeletal Muscle Protein Synthesis in Healthy, Middle-Aged Women.J Nutr. 2024 Dec;154(12):3626-3638. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.10.010. Epub 2024 Oct 11. J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39396760 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hector AJ, Marcotte GR, Churchward-Venne TA, Murphy CH, Breen L, von Allmen M, et al. Whey protein supplementation preserves postprandial myofibrillar protein synthesis during short-term energy restriction in overweight and obese adults. J Nutr. 2014;145(2):246–252. doi: 10.3945/jn.114.200832. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
