Improvement of intestinal flora: accompany with the antihypertensive effect of electroacupuncture on stage 1 hypertension
- PMID: 33413552
- PMCID: PMC7792359
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-020-00417-8
Improvement of intestinal flora: accompany with the antihypertensive effect of electroacupuncture on stage 1 hypertension
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence have indicated the relationship between intestinal dysbiosis and hypertension. We aimed to evaluate the effect of the electroacupuncture (EA) on intestinal microbiota in patients with stage 1 hypertension.
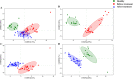
Methods: 93 hypertensive patients and 15 healthy subjects were enrolled in this study. Applying a highly accurate oscillometric device to evaluate the antihypertensive effect of EA. 16S rRNA sequencing was used to profile stool microbial communities from Healthy group, Before treatment (BT) group and After treatment (AT) group, and various multivariate analysis approaches were used to assess diversity, composition and abundance of intestinal microbiota.
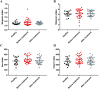
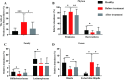
Results: In this study, EA significantly decreased the blood pressure (BP) of hypertensive patients. Higher abundance of Firmicutes and lower Bacteroidetes abundance were observed in the BT group compared to the Healthy group. And EA treatment significantly decreased the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio compared to the BT group. Moreover, at the genus level, there was an increased abundance of Escherichia-Shigella in patients with hypertension, while Blautia were decreased, and EA reversed these changes.
Conclusions: Our study indicates that EA can effectively lower BP and improve the structure of intestinal microbiota which are correlate with the alteration of blood pressure by electroacupuncture.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrial.gov, NCT01701726. Registered 5 October 2012, https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01701726.
Keywords: Dysbiosis; Electro-acupuncture; Intestinal flora; Stage 1 hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 81590950/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873383/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2012CB518501/National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program)
- 18YYJC0095/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province
- 2018JY0482/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

