Symptomatic aortitis at giant cell arteritis diagnosis: a prognostic factor of aortic event
- PMID: 33413605
- PMCID: PMC7792092
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-020-02396-5
Symptomatic aortitis at giant cell arteritis diagnosis: a prognostic factor of aortic event
Abstract
Background: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is frequently associated with aortic involvement that is likely to cause life-threatening structural complications (aneurysm, dissection). Few studies have investigated the occurrence of these complications, and no predictive factor has been identified so far. The aim of this study was to investigate factors associated with the risk of aortic complications in a cohort of GCA aortitis.
Methods: Data of all patients managed with aortitis (CT or 18 FDG PET) at the diagnosis of GCA in five hospitals from May 1998 and April 2019 were retrospectively collected. Clinical features were compared according to the presence of aortitis symptoms. The predictive factors of occurrence or aggravation of aortic structural abnormalities were investigated.
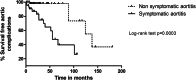
Results: One hundred and seventy-one patients with GCA aortitis were included; 55 patients (32%) had symptoms of aortitis (dorsal/lumbar/abdominal pain, aortic insufficiency) at diagnosis. The median follow-up was 38 months. Aortic complications occurred after a median time of 32 months. There were 19 new aortic aneurysms or complications of aneurysm and 5 dissections. Survival without aortic complication was significantly different between the symptomatic and non-symptomatic groups (Log rank, p = 0.0003). In multivariate analysis the presence of aortitis symptoms at diagnosis (HR 6.64 [1.95, 22.6] p = 0.002) and GCA relapse (HR 3.62 [1.2, 10.9] p = 0.02) were factors associated with the occurrence of aortic complications.
Conclusion: In this study, the presence of aortitis symptoms at the diagnosis of GCA aortitis and GCA relapse were independent predictive factors of occurrence of aortic complications during follow-up.
Keywords: Aneurysm; Aortic dissection; Aortitis; Giant cell arteritis; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Prieto-González S, Arguis P, García-Martínez A, Espígol-Frigolé G, Tavera-Bahillo I, Butjosa M, et al. Large vessel involvement in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis: prospective study in 40 newly diagnosed patients using CT angiography. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; [cited 2012 Jan 21]; Available from: http://ard.bmj.com/content/early/2012/01/20/annrheumdis-2011-200865.abst.... - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous