Effect of Travel Restrictions of Wuhan City Against COVID-19: A Modified SEIR Model Analysis
- PMID: 33413723
- PMCID: PMC8027550
- DOI: 10.1017/dmp.2021.5
Effect of Travel Restrictions of Wuhan City Against COVID-19: A Modified SEIR Model Analysis
Abstract
Objective: Since December 2019, a new coronavirus viral was initially detected in Wuhan, China. Population migration increases the risk of epidemic transmission. Here, the objective of study is to estimate the output risk quantitatively and evaluate the effectiveness of travel restrictions of Wuhan city.
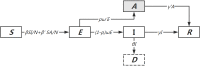
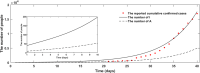
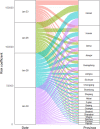
Methods: We proposed a modified susceptible-exposed-infectious-recovered (SEIR) dynamics model to predict the number of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) symptomatic and asymptomatic infections in Wuhan. And, subsequently, we estimated the export risk of COVID-19 epidemic from Wuhan to other provinces in China. Finally, we estimated the effectiveness of travel restrictions of Wuhan city quantitatively by the export risk on the assumption that the measure was postponed.
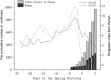
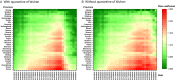
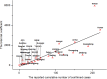
Results: The export risks of COVID-19 varied from Wuhan to other provinces of China. The peak of export risk was January 21-23, 2020. With the travel restrictions of Wuhan delayed by 3, 5, and 7 d, the export risk indexes will increase by 38.50%, 55.89%, and 65.63%, respectively.
Conclusions: The results indicate that the travel restrictions of Wuhan reduced the export risk and delayed the overall epidemic progression of the COVID-19 epidemic in China. The travel restrictions of Wuhan city may provide a reference for the control of the COVID-19 epidemic all over the world.
Keywords: COVID-19; SEIR model; export risk; migration indexes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 5;10:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3:CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. PMID: 33502002 Updated.
-
An evaluation of COVID-19 transmission control in Wenzhou using a modified SEIR model.Epidemiol Infect. 2021 Jan 8;149:e2. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820003064. Epidemiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33413715 Free PMC article.
-
International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 25;3(3):CD013717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013717.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33763851 Free PMC article.
-
When will the battle against novel coronavirus end in Wuhan: A SEIR modeling analysis.J Glob Health. 2020 Jun;10(1):011002. doi: 10.7189/jogh.10.011002. J Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32257174 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of quarantine of Wuhan city against the Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A well-mixed SEIR model analysis.J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):841-848. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25827. Epub 2020 Apr 25. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32243599
Cited by
-
Transmission dynamics model and the coronavirus disease 2019 epidemic: applications and challenges.Med Rev (2021). 2022 Feb 28;2(1):89-109. doi: 10.1515/mr-2021-0022. eCollection 2022 Feb 1. Med Rev (2021). 2022. PMID: 35658113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Cases Reported on International Arriving and Domestic Flights: United States, January 2020-December 2021.Am J Public Health. 2023 Aug;113(8):904-908. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2023.307325. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Am J Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37319391 Free PMC article.
-
Using search trends to analyze web-based users' behavior profiles connected with COVID-19 in mainland China: infodemiology study based on hot words and Baidu Index.PeerJ. 2022 Nov 9;10:e14343. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14343. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36389414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Health Commission of Hubei Provincial. Bulletin on the current situation of pneumonia in Wuhan. Published December 31, 2019. http://wjw.hubei.gov.cn/fbjd/dtyw/201912/t20191231_1822343.shtml. Accessed June 24, 2020.
-
- Health Commission of Hubei Provincial Website. The pathogen of pneumonia is a novel coronavirus. Published January 15, 2020. http://wjw.hubei.gov.cn/bmdt/mtjj/mtgz/202001/t20200114_1911969.shtml. Accessed June 24, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO to accelerate research and innovation for new coronavirus. Published June 24, 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/06-02-2020-who-to-accelerate-resear.... Accessed June 24, 2020.
-
- Health Commission of People’s Republic of China. The latest situation report of the new coronavirus pneumonia epidemic situation as of 23 June. Published June 24, 2020. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202006/bbd1e4755cc347179995feefbfaec6ab.s.... Accessed June 24, 2020.
-
- Word Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. Published June 24, 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed June 24, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

