Neuroimaging Offers Low Yield in Children Positive for SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33414225
- PMCID: PMC8115373
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A7022
Neuroimaging Offers Low Yield in Children Positive for SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
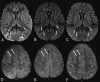
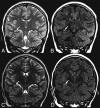
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus disease 2 (SARS CoV-2) most commonly presents with respiratory disease, but neurologic complications are being reported. We aimed to investigate the rate of positive neuroimaging findings in children positive for SARS-CoV-2 referred for neuroimaging between March 18 and September 30, 2020. We found that 10% (n = 2) had acute findings. Our results may suggest that in children, neurologic involvement in COVID-19 is rare, neuroimaging has a low yield in diagnosis, and acute neuroimaging should involve careful risk-benefit analysis.
© 2021 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain magnetic resonance imaging findings in children with neurological complications of coronavirus disease 2019 (Omicron variant): a multicenter retrospective observational study.Pediatr Radiol. 2024 May;54(6):1012-1021. doi: 10.1007/s00247-024-05908-6. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Pediatr Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38538753
-
Neuroimaging manifestations in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multinational, multicentre collaborative study.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021 Mar;5(3):167-177. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30362-X. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021. PMID: 33338439 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroradiologic manifestations of COVID-19: what the emergency radiologist needs to know.Emerg Radiol. 2020 Dec;27(6):737-745. doi: 10.1007/s10140-020-01840-y. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Emerg Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32822060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: a review.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 Feb;41(1):36-55. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1781356. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 32584199 Review.
-
Severity of Chest Imaging is Correlated with Risk of Acute Neuroimaging Findings among Patients with COVID-19.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021 May;42(5):831-837. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7032. Epub 2021 Feb 4. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 33541897 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neurological effects of COVID-19 in infants and children.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2022 Jul;64(7):818-829. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15185. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35243616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Fatigue. 2023;11(2-4):55-65. doi: 10.1080/21641846.2022.2162764. Epub 2023 Jan 1. Fatigue. 2023. PMID: 38044956 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Associated with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in a Child with Covid-19 and Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Case Report.Pulm Ther. 2022 Sep;8(3):333-342. doi: 10.1007/s41030-022-00192-x. Epub 2022 May 24. Pulm Ther. 2022. PMID: 35608797 Free PMC article.
-
Brain magnetic resonance imaging findings in children with neurological complications of coronavirus disease 2019 (Omicron variant): a multicenter retrospective observational study.Pediatr Radiol. 2024 May;54(6):1012-1021. doi: 10.1007/s00247-024-05908-6. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Pediatr Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38538753
-
Topographical Distribution of Neuroanatomical Abnormalities Following COVID-19 Invasion : A Systematic Literature Review.Clin Neuroradiol. 2024 Mar;34(1):13-31. doi: 10.1007/s00062-023-01344-5. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Clin Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 37697012 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
