MEX3A contributes to development and progression of glioma through regulating cell proliferation and cell migration and targeting CCL2
- PMID: 33414423
- PMCID: PMC7791131
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03307-x
MEX3A contributes to development and progression of glioma through regulating cell proliferation and cell migration and targeting CCL2
Abstract
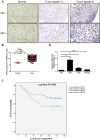
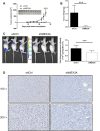
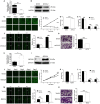
Glioma is one of the most commonly diagnosed intracranial malignant tumors with extremely high morbidity and mortality, whose treatment was seriously limited because of the unclear molecular mechanism. In this study, in order to identify a novel therapeutic target for glioma treatment, we explored the functions and mechanism of MEX3A in regulating glioma. The immunohistochemical staining of MEX3A in glioma and normal tissues revealed the upregulation of MEX3A and further indicated the relationship between high MEX3A expression and higher malignancy as well as poorer prognosis of glioma. In vitro loss-of-function and gain-of-function experiments comprehensively demonstrated that MEX3A may promote glioma development through regulating cell proliferation, cell apoptosis, cell cycle, and cell migration. In vivo experiments also suggested the inhibition of glioma growth by MEX3A knockdown. Moreover, our mechanistic study identifies CCL2 as a potential downstream target of MEX3A, which possesses similar regulatory effects on glioma development with MEX3A and could attenuate the promotion of glioma induced by MEX3A overexpression. Overall, MEX3A was identified as a potential tumor promoter in glioma development and therapeutic target in glioma treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The RNA binding protein MEX3A promotes tumor progression of breast cancer by post-transcriptional regulation of IGFBP4.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Oct;201(3):353-366. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07028-5. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37433992 Free PMC article.
-
MEX3A is upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and promotes development and progression of ESCC through targeting CDK6.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 14;12(21):21091-21113. doi: 10.18632/aging.103196. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33188661 Free PMC article.
-
MEX3A promotes development and progression of breast cancer through regulation of PIK3CA.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Jul 1;404(1):112580. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112580. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33811903
-
Mex3a promotes oncogenesis through the RAP1/MAPK signaling pathway in colorectal cancer and is inhibited by hsa-miR-6887-3p.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Jun;41(6):472-491. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12149. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33638620 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic Potential of the Dual-Function Protein MEX3A.Biology (Basel). 2021 May 7;10(5):415. doi: 10.3390/biology10050415. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067172 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Colon Cancer-Related RNAs Based on Heterogeneous Networks and Random Walk.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 2;11(7):1003. doi: 10.3390/biology11071003. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36101384 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitylation of RUNX3 by RNA-binding ubiquitin ligase MEX3C promotes tumorigenesis in lung adenocarcinoma.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 29;22(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04700-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38424632 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA binding protein MEX3A promotes tumor progression of breast cancer by post-transcriptional regulation of IGFBP4.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Oct;201(3):353-366. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07028-5. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37433992 Free PMC article.
-
MEX3A promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression via the miR-3163/SCIN axis by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Apr 30;13(4):420. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04871-0. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35490173 Free PMC article.
-
MEX3A determines in vivo hepatocellular carcinoma progression and induces resistance to sorafenib in a Hippo-dependent way.Hepatol Int. 2023 Dec;17(6):1500-1518. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10565-2. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Hepatol Int. 2023. PMID: 37460832
References
-
- Minniti G, Muni R, Lanzetta G, Marchetti P, Enrici RM. Chemotherapy for glioblastoma: current treatment and future perspectives for cytotoxic and targeted agents. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:5171–5184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

