STING promotes senescence, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via the NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 33414452
- PMCID: PMC7791051
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03341-9
STING promotes senescence, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via the NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
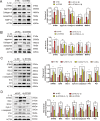
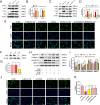
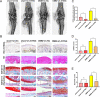
Damaged deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a primary pathologic factor for osteoarthritis (OA); however, the mechanism by which DNA damage drives OA is unclear. Previous research demonstrated that the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) participates in DNA damage response. As a result, the current study aimed at exploring the role STING, which is the major effector in the cGAS-STING signaling casacde, in OA progress in vitro, as well as in vivo. In this study, the expression of STING was evaluated in the human and mouse OA tissues, and in chondrocytes exposed to interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). The influences of STING on the metabolism of the extracellular matrix (ECM), apoptosis, and senescence, were assessed in STING overexpressing and knocking-down chondrocytes. Moreover, the NF-κB-signaling casacde and its role in the regulatory effects of STING on ECM metabolism, apoptosis, and senescence were explored. The STING knockdown lentivirus was intra-articularly injected to evaluate its therapeutic impact on OA in mice in vivo. The results showed that the expression of STING was remarkably elevated in the human and mouse OA tissues and in chondrocytes exposed to IL-1β. Overexpression of STING promoted the expression of MMP13, as well as ADAMTS5, but suppressed the expression of Aggrecan, as well as Collagen II; it also enhanced apoptosis and senescence in chondrocytes exposed to and those untreated with IL-1β. The mechanistic study showed that STING activated NF-κB signaling cascade, whereas the blockage of NF-κB signaling attenuated STING-induced apoptosis and senescence, and ameliorated STING-induced ECM metabolism imbalance. In in vivo study, it was demonstrated that STING knockdown alleviated destabilization of the medial meniscus-induced OA development in mice. In conclusion, STING promotes OA by activating the NF-κB signaling cascade, whereas suppression of STING may provide a novel approach for OA therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Lycopodium japonicum Thunb. inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis, senescence and inflammation in osteoarthritis through STING/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118660. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118660. Epub 2024 Aug 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39121926
-
Amentoflavone maintaining extracellular matrix homeostasis and inhibiting subchondral bone loss in osteoarthritis by inhibiting ERK, JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Oct 15;19(1):662. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05075-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39407273 Free PMC article.
-
SERPINF1 knockdown attenuates chondrocyte senescence, hypertrophy, and inflammation in osteoarthritis to offer a potential therapeutic strategy.Cell Signal. 2025 Aug;132:111840. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111840. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40306348
-
Unravelling the interplay between ER stress, UPR and the cGAS-STING pathway: Implications for osteoarthritis pathogenesis and treatment strategy.Life Sci. 2024 Nov 15;357:123112. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123112. Epub 2024 Oct 6. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39378929 Review.
-
Therapeutic targets in aging-related osteoarthritis: A focus on the extracellular matrix homeostasis.Life Sci. 2025 May 1;368:123487. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123487. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39978589 Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated M1 macrophage-dependent nanomedicine remodels inflammatory microenvironment for osteoarthritis recession.Bioact Mater. 2023 Dec 8;33:545-561. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.10.032. eCollection 2024 Mar. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 38162513 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory mechanism of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase on inflammatory senescence of nucleus pulposus cell.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Jul 22;19(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04919-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39034400 Free PMC article.
-
GAS-STING: a classical DNA recognition pathways to tumor therapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 18;14:1200245. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1200245. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37920470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell transcriptome and crosstalk analysis reveals immune alterations and key pathways in the bone marrow of knee OA patients.iScience. 2024 Aug 26;27(9):110827. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110827. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39310769 Free PMC article.
-
STING Is Required in Conventional Dendritic Cells for DNA Vaccine Induction of Type I T Helper Cell- Dependent Antibody Responses.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 22;13:861710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.861710. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35529875 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

