Efficacy and safety of the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist treatment for central serous chorioretinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33414535
- PMCID: PMC8115590
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-020-01338-4
Efficacy and safety of the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist treatment for central serous chorioretinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the efficacy and safety of the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) treatment for central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC).
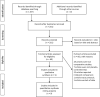
Methods: We searched the PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library to identify relevant clinical studies published prior to March 2020. The primary outcome was change in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), and the secondary outcomes included the subretinal fluid (SRF), subfoveal choroidal thickness (SFCT), and central macular thickness (CMT).
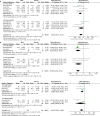
Results: Five randomized controlled trials (RCT) and four cohort studies met the inclusion criteria with a total of 352 eyes. The MRA treatment was not superior to placebo in BCVA at 1 month (WMD = -0.06, 95% CI -0.15-0.02, P = 0.15, I2 = 86%), 3 months (WMD = -0.04, 95% CI -0.14-0.06, P = 0.44, I2 = 77%) and 6 months (WMD = -0, 95% CI -0.05-0.05, P = 0.92, I2 = 0%). The MRA treatment resulted in significant reduction than the placebo in the SRF (WMD = -60.64, 95% CI -97.91 to -23.37, P = 0.001, I2 = 49%), SFCT (WMD = -39.15, 95% CI -52.58 to -25.72, P < 0.001, I2 = 0%), and CMT (WMD = -60.75, 95% CI -97.85 to -23.65, P = 0.01, I2 = 53%).
Conclusions: Our meta-analysis shows that the MRA treatment can improve anatomical structure in CSC patients, but it is not effective for achieving BCVA gain. The applicant of the MRA is safe and have no severe effect.
摘要: 目的: 通过meta分析, 研究醛固酮受体拮抗剂(mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, MRA) 治疗中心性浆液性脉络膜视网膜病变(central serous chorioretinopathy, CSC)的疗效和安全性。方法: 检索PubMed、Embase和the Cochrane Library数据库, 收集关于MRA治疗CSC的相关临床研究, 检索截止日期为2020年3月。主要结局指标为最佳矫正视力(best-corrected visual acuity, BCVA)的变化, 次要结局指标为视网膜下积液的厚度(subretinal fluid, SRF)、中心凹下脉络膜的厚度(subfoveal choroidal thickness, SFCT)和中心凹下视网膜的厚度(central macular thickness, CMT)。结果: 共纳入5篇随机对照研究和4篇队列研究, 包括352只眼。与空白对照组比较, 使用MRA治疗CSC 1月(WMD = −0.06, 95% CI −0.15–0.02, P = 0.15, I2 = 86%)、3月(WMD = −0.04, 95% CI −0.14–0.06, P = 0.44, I2 = 77%)和6月(WMD = −0, 95% CI −0.05–0.05, P = 0.92, I2 = 0%)的BCVA变化并无显著差异。但使用MRA进行治疗, 可以明显的减少SRF(WMD = −60.64, 95% CI −97.91∼−23.37, P = 0.001, I2 = 49%)、SFCT(WMD = −39.15, 95% CI −52.58∼−25.72, P < 0.001, I2 = 0%) 和CMT(WMD = −60.75, 95% CI −97.85∼−23.65, P = 0.01, I2 = 53%)。结论: 我们的研究结果表明, MRA治疗可以显著的促进CSC患者眼底解剖结构的恢复, 但对于其视力无明显的改善作用。.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chen L, Zhang P. Advances in the treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy. Int Eye Sci. 2020;20:79–82.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

