A cross-platform approach identifies genetic regulators of human metabolism and health
- PMID: 33414548
- PMCID: PMC7612925
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-020-00751-5
A cross-platform approach identifies genetic regulators of human metabolism and health
Abstract
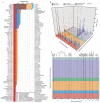
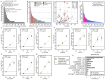
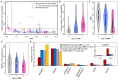
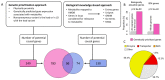
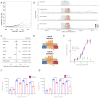
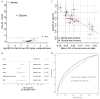
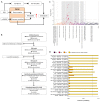
In cross-platform analyses of 174 metabolites, we identify 499 associations (P < 4.9 × 10-10) characterized by pleiotropy, allelic heterogeneity, large and nonlinear effects and enrichment for nonsynonymous variation. We identify a signal at GLP2R (p.Asp470Asn) shared among higher citrulline levels, body mass index, fasting glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide and type 2 diabetes, with β-arrestin signaling as the underlying mechanism. Genetically higher serine levels are shown to reduce the likelihood (by 95%) and predict development of macular telangiectasia type 2, a rare degenerative retinal disease. Integration of genomic and small molecule data across platforms enables the discovery of regulators of human metabolism and translation into clinical insights.
Conflict of interest statement
A.S.B. has received grants from AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bioverativ, Merck, Novartis, and Sanofi. J. D. sits on the International Cardiovascular and Metabolic Advisory Board for Novartis (since 2010), the Steering Committee of UK Biobank (since 2011), the MRC International Advisory Group (ING) member, London (since 2013), the MRC High Throughput Science ‘Omics Panel Member, London (since 2013), the Scientific Advisory Committee for Sanofi (since 2013), the International Cardiovascular and Metabolism Research and Development Portfolio Committee for Novartis and the Astra Zeneca Genomics Advisory Board (2018). E.B.F. is an employee and stock holder of Pfizer.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12012/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00011/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_13030/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N003284/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0500300/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00014/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BTRU-2014-10024/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 106263/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_13046/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 14136/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 106262/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 204623/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A090_1006/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00006/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_13048/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SP/09/002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/P011705/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/18/13/33946/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12012/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 204623/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- C864/A14136/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00002/7/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L00002/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT083442AIA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CH/12/2/29428/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/S003746/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00014/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/13/13/30194/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/S019669/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P01836X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

