Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy for Achieving R0
- PMID: 33414613
- PMCID: PMC7739842
- DOI: 10.4293/JSLS.2020.00060
Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy for Achieving R0
Abstract
Background: Minimally invasive esophagectomy (MIE) is becoming increasing popular. Since it was introduced, there has been debate about its safety and efficacy when compared with open esophagectomies (OE). We sought to compare the oncologic outcomes of MIE and OE in this study specifically with regards to margin status and nodal retrieval.
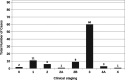
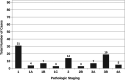
Methods: Ninety-three patients that underwent MIE (76/93) or OE (17/93) for esophageal cancer at out institution between January 2013 and September 2018 were retrospectively reviewed. Histological type, pathological tumor grading, clinical tumor staging (cTNM), pathological tumor staging (pTNM), post-neoadjuvant tumor staging (ypTNM), and lymph node retrieval were obtained and compared.
Results: The results show a statistically significant improvement in resection margins (R0) in the MIE group when compared with the OE group. Other oncologic parameters including clinical staging, pathologic staging, tumor grade, neoadjuvant therapy (NAT), and nodal retrieval were not statistically significantly different between the open and MIE groups.
Conclusion: The improvement in short-term surgical outcomes in MIE is well established. This study demonstrates that MIE can have superior surgical oncologic outcomes compared to OE, this was specifically an improved R0 margin rate with MIE compared to OE. These results further support the use of MIE in the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Keywords: Esophageal Cancer; Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy; Oncologic Outcome; Open Esophagectomy; Robotic-assisted Esophagectomy.
© 2020 by JSLS, Journal of the Society of Laparoscopic & Robotic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of surgical approach on perioperative and long-term outcomes following esophagectomy for esophageal cancer.Surg Endosc. 2018 Apr;32(4):1892-1900. doi: 10.1007/s00464-017-5881-6. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Surg Endosc. 2018. PMID: 29067584
-
Comparisons between minimally invasive and open esophagectomy for esophageal cancer with cervical anastomosis: a retrospective study.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020 Jun 8;15(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13019-020-01182-3. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020. PMID: 32513211 Free PMC article.
-
Nationwide analysis of short-term surgical outcomes of minimally invasive esophagectomy for malignancy.Int J Surg. 2016 Jan;25:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.11.023. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Int J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26602969 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive esophagectomy for esophageal cancer: an updated review.Surg Today. 2013 Mar;43(3):237-44. doi: 10.1007/s00595-012-0300-z. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Surg Today. 2013. PMID: 22926551 Review.
-
Robotic-assisted minimally invasive esophagectomy versus the conventional minimally invasive one: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Int J Med Robot. 2019 Jun;15(3):e1988. doi: 10.1002/rcs.1988. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Int J Med Robot. 2019. PMID: 30737881
Cited by
-
Intraoperative fluorescence imaging in esophagectomy and its application to the robotic platform: a narrative review.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Sep;14(9):3598-3605. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-456. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 36245633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Esophagectomy in octogenarians: is it at a cost?Heliyon. 2022 Nov 28;8(12):e11945. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11945. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36478793 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of transthoracic esophagectomy with a next-generation surgical robot.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 26;12(1):17925. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21323-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36289257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Esophageal Cancer. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/esophagus-cancer/about/key-statistics.html. Accessed June 7, 2020.
-
- Devesa SS, Blot WJ, Fraumeni Jr JF. Changing patterns in the incidence of esophageal and gastric carcinoma in the United States. Cancer.1998. Nov 15;83(10):2049-2053. - PubMed
-
- Berlth F, Plum PS, Chon SH, Gutschow CA, Bollschweiler E, Hölscher AH. Total minimally invasive esophagectomy for esophageal adenocarcinoma reduces postoperative pain and pneumonia compared to hybrid esophagectomy. Surg Endosc. 2018. Dec 1;32(12):4957-4965. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical