Telmisartan Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System, Compared With Standard Telmisartan, More Effectively Improves Hepatic Fibrosis in Rats
- PMID: 33414695
- PMCID: PMC7750776
- DOI: 10.1177/1559325820982190
Telmisartan Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System, Compared With Standard Telmisartan, More Effectively Improves Hepatic Fibrosis in Rats
Abstract
Background: This study was designed to examine effects of telmisartan; an angiotensin receptor blocker; self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) in reversing already-established hepatic fibrosis.
Method: Forty rats were given thioacetamide (200 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) twice/week for 8 weeks then divided into 5 groups (n = 8), PC and 4 treated groups. Treatments were given orally for another 2 months as follows: telmisartan low and high doses (TL and TH: 1.8 and 3.6 mg/kg/day) and telmisartan SNEDDS at the same doses (TLS and THS). At end of treatment, blood was obtained and liver was isolated.
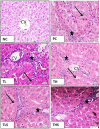
Results: Rats showed significant elevations of plasma ALT and AST and hepatic IL-6, TNF-α, and MDA, significant reductions of plasma albumin, hepatic GSH, and body weight, and hepatic histopathological damage. All treatments except for TL significantly reversed these thioacetamide-induced changes. THS group showed significant differences from all groups. Regarding ratio of free telmisartan concentration in hepatic homogenate to that of plasma, TH and TLS groups showed non-significant variation between each other while THS group showed significant differences from them. No significant changes were detected in blood pressure, hemoglobin, white blood cells, and platelets.
Conclusion: Telmisartan SNEDDS, compared with telmisartan, more effectively reversed chronic hepatic fibrosis with good safety profile.
Keywords: liver fibrosis; telmisartan; thioacetamide.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Candesartan, rather than losartan, improves motor dysfunction in thioacetamide-induced chronic liver failure in rats.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017 Sep 21;50(11):e6665. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20176665. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017. PMID: 28953991 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the angiotensin II receptor, type 1 receptor antagonists, losartan and telmisartan, on thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Aug;67(4):575-586. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27779478
-
Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System of Coenzyme (Q10) with Improved Dissolution, Bioavailability, and Protective Efficiency on Liver Fibrosis.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017 Jul;18(5):1657-1672. doi: 10.1208/s12249-016-0632-x. Epub 2016 Sep 27. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017. PMID: 27677262
-
Mesalazine, an osteopontin inhibitor: The potential prophylactic and remedial roles in induced liver fibrosis in rats.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Jun 1;289:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 5. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29738702
-
Does telmisartan prevent hepatic fibrosis in rats with alloxan-induced diabetes?Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Jul 1;614(1-3):146-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.04.042. Epub 2009 May 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19406119
Cited by
-
Radiation Induced Skin Fibrosis (RISF): Opportunity for Angiotensin II-Dependent Intervention.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 29;25(15):8261. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158261. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel nano-formulation of olmesartan medoxomil with improved delivery and efficacy in the treatment of indomethacin-induced duodenitis in rats.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023 May 29;56:e12665. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2023e12665. eCollection 2023. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 37255094 Free PMC article.
-
Olmesartan medoxomil self-microemulsifying drug delivery system reverses apoptosis and improves cell adhesion in trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in rats.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2017-2028. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2086939. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35766160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakayama S, Watada H, Mita T, et al. Comparison of effects of olmesartan and telmisartan on blood pressure and metabolic parameters in Japanese early-stage type-2 diabetics with hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2008;31(1):7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

