CTRP5-Overexpression Attenuated Ischemia-Reperfusion Associated Heart Injuries and Improved Infarction Induced Heart Failure
- PMID: 33414720
- PMCID: PMC7783420
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.603322
CTRP5-Overexpression Attenuated Ischemia-Reperfusion Associated Heart Injuries and Improved Infarction Induced Heart Failure
Abstract
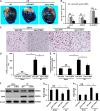
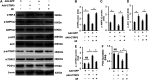
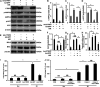
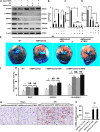
Aims: C1q/tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related protein 5 (CTRP5) belongs to the C1q/TNF-α related protein family and regulates glucose, lipid metabolism, and inflammation production. However, the roles of CTRP5 in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) associated with cardiac injuries and heart failure (HF) needs to be elaborated. This study aimed to investigate the roles of CTRP5 in I/R associated cardiac injuries and heart failure. Materials and Methods: Adeno-associated virus serum type 9 (AAV9)vectors were established for CTRP5 overexpression in a mouse heart (AAV9-CTRP5 mouse). AAV9-CTRP5, AMPKα2 global knock out (AMPKα2-/-)and AAV9-CTRP5+ AMPKα2-/- mice were used to establish cardiac I/R or infarction associated HF models to investigate the roles and mechanisms of CTRP5 in vivo. Isolated neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMS) transfected with or without CTRP5 adenovirus were used to establish a hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/O) model to study the roles and mechanisms of CTRP5 in vitro. Key Findings: CTRP5 was up-regulated after MI but was quickly down-regulated. CTRP5 overexpression significantly decreased I/R induced IA/AAR and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and attenuated infarction area, and improved cardiac functions. Mechanistically, CTRP5 overexpression markedly increased AMPKα2 and ACC phosphorylation and PGC1-α expression but inhibited mTORC1 phosphorylation. In in vitro experiments, CTRP5 overexpression could also enhance AMPKα2 and ACC phosphorylation and protect against H/O induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis. Finally, we showed that CTPR5 overexpression could not protect against I/R associated cardiac injuries and HF in AMPKα2-/- mice. Significance: CTRP5 overexpression protected against I/R induced mouse cardiac injuries and attenuated myocardial infarction induced cardiac dysfunction by activating the AMPKαsignaling pathway.
Keywords: CTPR5; heart; heart failure; ischemia/reperfusion; myocardial infarction.
Copyright © 2020 Peng, Liu, Zhang, Xu, Zhao and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of AMPKα2 attenuated doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via inhibiting lipid peroxidation associated ferroptosis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 Aug 20;205:275-290. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.06.004. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37331642
-
AMPKα2 Protects Against the Development of Heart Failure by Enhancing Mitophagy via PINK1 Phosphorylation.Circ Res. 2018 Mar 2;122(5):712-729. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.312317. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 29284690 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of AMPKα2 Blocked the Protection of Sestrin2 Overexpression Against Cardiac Hypertrophy Induced by Pressure Overload.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 17;12:716884. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.716884. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867324 Free PMC article.
-
AMPKα2 Overexpression Reduces Cardiomyocyte Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Normalization of Mitochondrial Dynamics.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 27;8:833. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00833. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32984328 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of TIMP3 Protects Against Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Myocardial Apoptosis Through ROS/Mapks Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(3):1011-1023. doi: 10.1159/000485401. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29179205
Cited by
-
Trimetazidine Attenuates Heart Failure by Improving Myocardial Metabolism via AMPK.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 15;12:707399. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.707399. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34603021 Free PMC article.
-
Role of serum C1q/TNF-related protein family levels in patients with acute coronary syndrome.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 19;9:967918. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.967918. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36061536 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Reveals DNA Damage and Cell Cycle Arrest as Hallmarks in Bicuspid Aortic Valve Patients.J Proteome Res. 2024 Aug 2;23(8):3012-3024. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00649. Epub 2024 Apr 9. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 38594816 Free PMC article.
-
Complement 1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Proteins (CTRPs): Structure, Receptors and Signaling.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 14;11(2):559. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020559. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CTRP5 Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity Via Inhibiting TLR4/NLRP3 Signaling.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Dec;38(6):1235-1244. doi: 10.1007/s10557-023-07464-x. Epub 2023 May 31. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 37256416
References
-
- Kambara T., Ohashi K., Shibata R., Ogura Y., Maruyama S., Enomoto T., et al. (2012). CTRP9 protein protects against myocardial injury following ischemia-reperfusion through AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 18965–18973. 10.1074/jbc.M112.357939 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

