Effects of Physical Exercise on Neuroplasticity and Brain Function: A Systematic Review in Human and Animal Studies
- PMID: 33414823
- PMCID: PMC7752270
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8856621
Effects of Physical Exercise on Neuroplasticity and Brain Function: A Systematic Review in Human and Animal Studies
Abstract
Background: Physical exercise (PE) has been associated with increase neuroplasticity, neurotrophic factors, and improvements in brain function.
Objective: To evaluate the effects of different PE protocols on neuroplasticity components and brain function in a human and animal model.
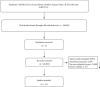
Methods: We conducted a systematic review process from November 2019 to January 2020 of the following databases: PubMed, ScienceDirect, SciELO, LILACS, and Scopus. A keyword combination referring to PE and neuroplasticity was included as part of a more thorough search process. From an initial number of 20,782 original articles, after reading the titles and abstracts, twenty-one original articles were included. Two investigators evaluated the abstract, the data of the study, the design, the sample size, the participant characteristics, and the PE protocol.
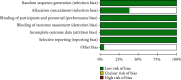
Results: PE increases neuroplasticity via neurotrophic factors (BDNF, GDNF, and NGF) and receptor (TrkB and P75NTR) production providing improvements in neuroplasticity, and cognitive function (learning and memory) in human and animal models.
Conclusion: PE was effective for increasing the production of neurotrophic factors, cell growth, and proliferation, as well as for improving brain functionality.
Copyright © 2020 Matheus Santos de Sousa Fernandes et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Martínez-Morga M., Quesada M. P., Bueno C. R., Martínez S. Bases neurobiológicas del autismo y modelos celulares para su estudio experimental. Medicina. 2019;79:27–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

