Pre-Exercise Maltodextrin Ingestion and Transient Hypoglycemia in Cycling and Running
- PMID: 33414865
- PMCID: PMC7745896
- DOI: 10.70252/OPRJ4508
Pre-Exercise Maltodextrin Ingestion and Transient Hypoglycemia in Cycling and Running
Abstract
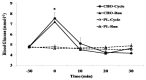
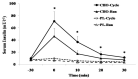
This study examined the phenomenon of transient hypoglycemia and metabolic responses to pre-exercise carbohydrate (CHO) maltodextrin ingestion in cycling and running on the same individuals. Eleven active males cycled or ran for 30 min at 80% maximal heart rate (HRmax) after ingestion of either 1g/kg body mass maltodextrin (CHO-Cycle and CHO-Run respectively) or placebo (PL-Cycle and PL-Run) solutions. Fluids were ingested 30min before exercise in a double-blind and random manner. Blood glucose and serum insulin were higher before exercise in CHO (mean CHO-Cycle+CHO-Run) (Glucose: 7.4 ± 0.3 mmol·l-1; Insulin: 59 ± 10 mU·l-1) compared to placebo (mean PL-Cycle+PL-Run) (Glucose: 4.7 ± 0.1 mmol·l-1; Insulin: 8 ± 1 mU·l-1) (p<0.01), but no differences were observed during exercise among the 4 conditions. Mean blood glucose did not drop below 4.1 mmol·l-1 in any trial. However, six volunteers in CHO-Cycle and seven in CHO-Run experienced blood glucose concentration ≤ 3.5 mmol·l-1 at 20min of exercise and similar degree of transient hypoglycemia in both exercise modes. No association was found between insulin response to maltodextrin ingestion and drop in blood glucose during exercise. Blood lactate increased with exercise more in cycling compared to running, and plasma free fatty acids (FFA) concentrations were higher in placebo compared to CHO irrespective of exercise mode (p<0.01). The ingestion of maltodextrin 30min before exercise at about 80% HRmax produced similar glucose and insulin responses in cycling and running in active males. Lactate was higher in cycling, whereas maltodextrin reduced FFA concentrations independently of exercise mode.
Keywords: Mode of exercise; carbohydrate; glucose; insulin; supplementation.
Figures

References
-
- Achten J, Jeukendrup AE. Effects of pre-exercise ingestion of carbohydrate on glycaemic and insulinaemic responses during subsequent exercise at differing intensities. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003;88(4–5):466–471. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom J, Hermansen L, Hultman E, Saltin B. Diet, muscle glycogen, and physical performance. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967;71(2):140–150. - PubMed
-
- Borg GAV. Perceived exertion: A note on “history” and methods. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1973;5(2):90–93. - PubMed
-
- Brietzke C, Franco-Alvarenga PE, Coelho-Junior HJ, Silveira R, Asano RY, Pires FO. Effects of carbohydrate mouth rinse on cycling time trial performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2019;49(1):57–66. - PubMed
-
- Carmen GY, Victor SM. Signalling mechanisms regulating lipolysis. Cell Signal. 2006;18(4):401–408. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
