Reflected Protons in the Lunar Wake and Their Effects on Wake Potentials
- PMID: 33415065
- PMCID: PMC7786520
- DOI: 10.1029/2020ja028154
Reflected Protons in the Lunar Wake and Their Effects on Wake Potentials
Abstract
The refilling of the lunar wake is facilitated by the wake ambipolar electric potential arising from the electron pressure gradient. Incident solar wind protons can be reflected by the lunar crustal magnetic fields and the lunar surface on the dayside and repicked up, entering the lunar wake due to their large gyroradii. This burst of positive charges can cause the lunar wake potential to be reduced by hundreds of volts. We utilize over 7 years of ARTEMIS (Acceleration, Reconnection, Turbulence, and Electrodynamics of the Moon's Interaction with the Sun) measurements to systematically investigate how the reflected protons affect the lunar wake potential structure when the Moon is immersed in the solar wind. RPs have a peak occurrence rate of ~20% for downstream distances from the Moon at N × 2πR g and a preference of high occurrence rates and high densities in the direction of the motional electric field of the solar wind. We show that reflected protons in the lunar wake can significantly change the electrostatic ambipolar potentials in the wake, leading in turn to the formation of field-aligned, accelerated electron beams. Our case study also suggests a nonmonotonic field-aligned potential structure in the presence of reflected protons in the wake. Lastly, our results show that when the reflected proton density is larger than ~30% of the local proton density from refilling solar wind protons, the wake potential scales as the logarithmic density of reflected protons, which can be explained by the Boltzmann relation.
Figures
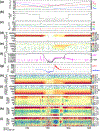
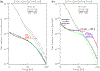
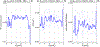
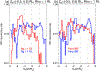
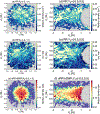

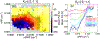
References
-
- Angelopoulos V (2011). The ARTEMIS mission. Space Science Reviews, 165, 3–25. 10.1007/s11214-010-9687-2 - DOI
-
- Auster H, Glassmeier K, Magnes W, Aydogar O, Baumjohann W, Constantinescu D, et al. (2008). The THEMIS fluxgate magnetometer. Space Science Reviews, 141(1–4), 235–264.
-
- Bonnell J, Mozer F, Delory G, Hull A, Ergun R, Cully C, et al. (2009). The electric field instrument (EFI) for THEMIS, The THEMIS mission (pp. 303–341). New York, NY: Springer.
-
- Chao J, Wu D, Lin C-H, Yang Y-H, Wang X, Kessel M, et al. (2002). Models for the size and shape of the Earth’s magnetopause and bow shock Cospar Colloquia series (Vol.12, pp. 127–135). Pergamon: Elsevier.
