Modeled Structure of the Cell Envelope Proteinase of Lactococcus lactis
- PMID: 33415101
- PMCID: PMC7783315
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.613986
Modeled Structure of the Cell Envelope Proteinase of Lactococcus lactis
Abstract
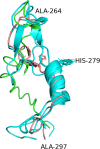
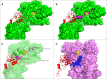
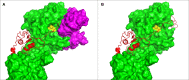
The cell envelope proteinase (CEP) of Lactococcus lactis is a large extracellular protease covalently linked to the peptidoglycan of the cell wall. Strains of L. lactis are typically auxotrophic for several amino acids and in order to grow to high cell densities in milk they need an extracellular protease. The structure of the entire CEP enzyme is difficult to determine experimentally due to the large size and due to the attachment to the cell surface. We here describe the use of a combination of structure prediction tools to create a structural model for the entire CEP enzyme of Lactococcus lactis. The model has implications for how the bacterium interacts with casein micelles during growth in milk, and it has implications regarding the energetics of the proteolytic system. Our model for the CEP indicates that the catalytic triad is activated through a structural change caused by interaction with the substrate. The CEP of L. lactis might become a useful model for the mode of action for enzymes belonging to the large class of S8 proteinases with a PA (protease associated) domain and a downstream fibronectin like domain.
Keywords: S8 proteinase; casein micelle; cell envelope associated peptidases; lactic acid bacteria (LAB); protein structure prediction; proteolytic system; substrate specificity; subtilisin.
Copyright © 2020 Hansen and Marcatili.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
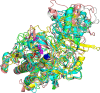





Similar articles
-
Classification of Lactococcus lactis cell envelope proteinase based on gene sequencing, peptides formed after hydrolysis of milk, and computer modeling.J Dairy Sci. 2015 Jan;98(1):68-77. doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-8517. Epub 2014 Nov 7. J Dairy Sci. 2015. PMID: 25465631
-
Engineering of the substrate-binding region of the subtilisin-like, cell-envelope proteinase of Lactococcus lactis.Protein Eng. 1993 Nov;6(8):927-37. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.8.927. Protein Eng. 1993. PMID: 8309942
-
Diversity of cell envelope proteinase specificity among strains of Lactococcus lactis and its relationship to charge characteristics of the substrate-binding region.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Nov;59(11):3640-7. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.11.3640-3647.1993. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 8285671 Free PMC article.
-
Original features of cell-envelope proteinases of Lactobacillus helveticus. A review.Int J Food Microbiol. 2011 Mar 15;146(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.01.039. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21354644 Review.
-
Proteinase genes of cheese starter cultures.Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Aug;19(3):670-4. doi: 10.1042/bst0190670. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991. PMID: 1783195 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Structure Analysis of the Multi-Domain, Cell Envelope Proteases of Lactic Acid Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 8;11(9):2256. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092256. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764099 Free PMC article.
-
Fermentation of plant-based dairy alternatives by lactic acid bacteria.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 May;15(5):1404-1421. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14008. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35393728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Colletotrichum nymphaeae-Strawberry interaction reveals in planta expressed genes associated with virulence.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 20;15:1390926. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1390926. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39925370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berhe T., Ipsen R., Seifu E., Kurtu M. Y., Eshetu M., Hansen E. B. (2018). Comparison of the acidification activities of commercial starter cultures in camel and bovine milk. LWT 89 123–127. 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.10.041 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

