Production of transglutaminase in glutathione-producing recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 33415535
- PMCID: PMC7790930
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-020-01176-3
Production of transglutaminase in glutathione-producing recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
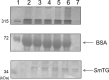
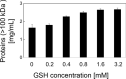
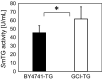
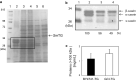
Transglutaminase (TG) catalyzes the formation of cross-links between proteins. TG from Streptoverticillium mobaraense (SmTG) is used widely in food, cosmetic, biomaterial and medical industries. SmTG is occasionally supplied as a mixture with the activator peptide glutathione. Currently, glutathione is industrially produced using a budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, because of its intracellular high content of glutathione. In this study, active SmTG was produced together with glutathione in S. cerevisiae. SmTG extracted from S. cerevisiae expressing SmTG showed cross-linking activity when BSA and sodium caseinate were substrates. The cross-linking activity of SmTG increased proportionally as the concentration of added glutathione increased. Furthermore, SmTG was prepared by extracting SmTG from an engineered S. cerevisiae whose glutathione synthetic pathway was enhanced. The SmTG solution showed higher activity when compared with a SmTG solution prepared from a S. cerevisiae strain without enhanced glutathione production. This result indicates that a high content of intracellular glutathione further enhances active SmTG production in S. cerevisiae. S. cerevisiae co-producing SmTG and a higher content of glutathione has the potential to supply a ready-to-use industrial active TG solution.
Keywords: Coproduction; Glutathione; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Streptoverticillium mobaraense; Transglutaminase; Yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ando H, Adachi M, Umeda K, Matsuura A, Nonaka M, Uchio R, Tanaka H, Motoki M. Purification and characteristics of a novel transglutaminase derived from microorganism. Agric Biol Chem. 1989;53:2613–2617.
-
- Bönisch MP, Lauber S, Kulozik U. Improvement of enzymatic cross-linking of casein micelles with transglutaminase by glutathione addition. Int Dairy J. 2007;17:3–11. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2006.01.007. - DOI
-
- Fox PF, Uniacke-Lowe T, McSweeney PLH, O'Mahony JA. Dairy chemistry and biochemistry. Glasgow: Blackie Academic & Professional; 1998.
Grants and funding
- 16K00616/Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology, MEXT, Japan, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C)
- JPMJMI17EJ/Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology, MEXT, Japan, Grant-in-Aid for Science and Technology, MEXT, Japan, Grant-in-Aid for the JST-Mirai Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

