Nebulized Magnesium Sulfate for Treatment of Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of Newborn: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33415555
- PMCID: PMC7790729
- DOI: 10.1007/s12098-020-03643-y
Nebulized Magnesium Sulfate for Treatment of Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of Newborn: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effectiveness of nebulized magnesium sulfate in treating persistent pulmonary hypertension of newborn (PPHN).
Methods: Twenty-eight mechanically ventilated term neonates with severe PPHN were randomized into two groups: NebMag group (n = 14), who receiving nebulized isotonic magnesium (1024 mg/h), and IVMag group (n = 14), who received intravenous magnesium (200 mg/kg over 30 min, followed by 50 mg/kg/h). The study time frame was 24 h. Outcome measures were the changes in oxygenation index (OI), mean arterial blood pressure (MABP), vasoactive inotropic score (VIS), and serum magnesium level.
Results: Baseline demographic, ventilatory, and hemodynamic characteristics were comparable between the two groups. At the end of the study, the OI decreased by 44.3% in the NebMag group compared with 35.3% in the IVMag group (mean difference -3.14; 95%CI -5.08, -1.19; p 0.003). The NebMag group had a higher MABP (mean difference 2.29 mmHg; 95% CI 1.80, 2.77; p 0.000) and lower VIS (mean difference -14.64; 95% CI -16.52, -12.77; p 0.000) at the 24-h study time point. The increase in serum magnesium level, measured at 12-h study time point, was lower in the NebMag group (mean difference -2.26 mmol/L; 95% CI -2.58, -1.96; p 0.000).
Conclusion: Nebulized magnesium sulfate may be an effective therapeutic modality for neonates with severe PPHN on mechanical ventilation, but this should be confirmed by larger studies. Retrospectively registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov (identifier: NCT04328636).
Keywords: Hypoxia; Magnesium; Nebulizer; Neonate; PPHN; Persistent fetal circulation.
© 2021. Dr. K C Chaudhuri Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


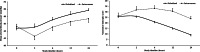
Comment in
-
Utility of Nebulized Magnesium Sulfate Therapy for Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of Newborn.Indian J Pediatr. 2021 Aug;88(8):749-750. doi: 10.1007/s12098-021-03851-0. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Indian J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34164785 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- El-Khuffash A, McNamara PJ, Breatnach C, et al. The use of milrinone in neonates with persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn - a randomised controlled trial pilot study (MINT 1): study protocol and review of literature. Matern Heal Neonatol Perinatol. 2018;4(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s40748-018-0093-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

