CDKN2A (p16INK4A) affects the anti‑tumor effect of CDK inhibitor in somatotroph adenomas
- PMID: 33416096
- PMCID: PMC7797444
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4807
CDKN2A (p16INK4A) affects the anti‑tumor effect of CDK inhibitor in somatotroph adenomas
Abstract
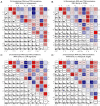
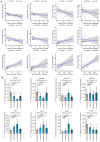
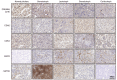
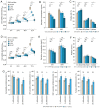
The altered cell cycle is associated with aberrant growth factor signaling in somatotroph adenoma, which is the primary cause of acromegaly. The aim of the present study was to investigate the pathological role of the INK4 family and evaluate the effectiveness of CDK4 inhibitor, palbociclib, in somatotroph adenoma. RNA‑Seq, RT‑PCR, and immunohistochemistry were applied to measure the levels and correlations of the INK4 family with angiogenesis, CDKs, EMT, and therapeutic targets. MTS, flow cytometry, and ELISA were used to investigate the bio‑activity in GH3 and GT1‑1 cell lines after palbociclib treatment. Compared with lactotroph adenoma, gonadotroph adenoma, and corticotroph adenoma, somatotroph samples demonstrated higher expression of CDKN2A and SSTR2 but a lower expression of EGFR, CDK4, and CDH2 (P<0.05). CDKN2A positively correlates with SSTR2, and negatively with CDK4, EGFR, and CDH2. Patients with lower CDKN2A had larger tumor size (P=0.016) and more invasive potential (P=0.023). Palbociclib inhibited cell proliferation, induced G1 phase arrest, reduced GH/IGF‑1 secretion of GH3 and GT1‑1 cell lines (P<0.05), and had a more prominent role in GH3 cells (P<0.05). CDKN2A inhibited the bio‑activity by modulating CDK4, and high CDKN2A predicted the insensitivity to CDK4 inhibitor, palbociclib, in somatotroph adenoma patients. In summary, the present study shows CDKN2A inhibited the bio‑activity by modulating CDK4, and high CDKN2A predicts the insensitivity to CDK4 inhibitor, Palbociclib, in somatotroph adenoma patients.
Keywords: somatotroph adenomas; INK4 family; CDKN2A (p16INK4A); palbociclib; CDK4.
Figures
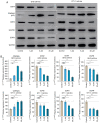
Similar articles
-
Direct CDKN2 Modulation of CDK4 Alters Target Engagement of CDK4 Inhibitor Drugs.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Apr;18(4):771-779. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0755. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 30837298
-
Regression of a nonfunctioning pituitary macroadenoma on the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib: case report.Neurosurg Focus. 2018 Jun;44(6):E9. doi: 10.3171/2018.2.FOCUS17660. Neurosurg Focus. 2018. PMID: 29852762
-
CDKN2A/p16 inactivation is related to pituitary adenoma type and size.J Pathol. 2001 Apr;193(4):491-7. doi: 10.1002/path.833. J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11276008
-
Cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitors including palbociclib as anticancer drugs.Pharmacol Res. 2016 May;107:249-275. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.03.012. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 26995305 Review.
-
Progress of CDK4/6 Inhibitor Palbociclib in the Treatment of Cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(9):1241-1251. doi: 10.2174/1871521409666170412123500. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28403773 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance and prospective mechanism of increased CDKN2A expression in small cell lung cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Jun;26(6):1519-1531. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03376-2. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38206516 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomic and transcriptomic landscaping unraveled candidate repositioned therapeutics for non-functioning pituitary neuroendocrine tumors.J Endocrinol Invest. 2023 Apr;46(4):727-747. doi: 10.1007/s40618-022-01923-2. Epub 2022 Oct 28. J Endocrinol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36306107
-
Next-Generation Sequencing Whole-Genome Analysis for Targeted Treatment Approach of Metastatic Bartholin Gland Adenocarcinoma: An Emblematic Case Report and Review of the Literature.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Nov 10;11(11):2085. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11112085. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neou M, Villa C, Armignacco R, Jouinot A, Raffin-Sanson ML, Septier A, Letourneur F, Diry S, Diedisheim M, Izac B, et al. Pangenomic classification of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Cell. 2019;13:S1535610819305227. - PubMed
-
- Melmed S, Popovic V, Bidlingmaier M, Mercado M, van der Lely AJ, Biermasz N, Bolanowski M, Coculescu M, Schopohl J, Racz K, et al. Safety and efficacy of oral octreotide in acromegaly: Results of a multicenter phase III trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:1699–1708. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-4113. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alquraini H, Del Pilar Schneider M, Mirakhur B, Barkan A. Biochemical efficacy of long-acting lanreotide depot/autogel in patients with acromegaly naïve to somatostatin-receptor ligands: Analysis of three multicenter clinical trials. Pituitary. 2018;21:283–289. doi: 10.1007/s11102-018-0867-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

