Transcriptomic landscaping of core genes and pathways of mild and severe psoriasis vulgaris
- PMID: 33416099
- PMCID: PMC7723513
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4771
Transcriptomic landscaping of core genes and pathways of mild and severe psoriasis vulgaris
Abstract
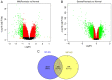
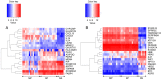
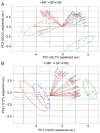
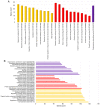
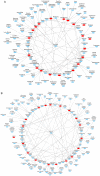
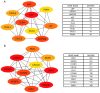
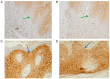
Psoriasis is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting >125 million individuals worldwide. The therapeutic course for the disease is generally designed upon the severity of the disease. In the present study, the gene expression profile GSE78097, was retrieved from the National Centre of Biotechnology (NCBI)‑Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database to explore the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in mild and severe psoriasis using the Affy package in R software. The Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways of the DEGs were analysed using clusterProfiler, Bioconductor, version 3.8. In addition, the STRING database was used to develop DEG‑encoded proteins and a protein‑protein interaction network (PPI). Cytoscape software, version 3.7.1 was utilized to construct a protein interaction association network and analyse the interaction of the candidate DEGs encoding proteins in psoriasis. The top 2 hub genes in Cytohubba plugin parameters were validated using immunohistochemical analysis in psoriasis tissues. A total of 382 and 3,001 dysregulated mild and severe psoriasis DEGs were reported, respectively. The dysregulated mild psoriasis genes were enriched in pathways involving cytokine‑cytokine receptor interaction and rheumatoid arthritis, whereas cytokine‑cytokine receptor interaction, cell cycle and cell adhesion molecules were the most enriched pathways in severe psoriasis group. PL1N1, TLR4, ADIPOQ, CXCL8, PDK4, CXCL1, CXCL5, LPL, AGT, LEP were hub genes in mild psoriasis, whereas BUB1, CCNB1, CCNA2, CDK1, CDH1, VEGFA, PLK1, CDC42, CCND1 and CXCL8 were reported hub genes in severe psoriasis. Among these, CDC42, for the first time (to the best of our knowledge), has been reported in the psoriasis transcriptome, with its involvement in the adaptive immune pathway. Furthermore, the immunoexpression of CDK1 and CDH1 proteins in psoriasis skin lesions were demonstrated using immunohistochemical analysis. On the whole, the findings of the present integrated bioinformatics and immunohistochemical study, may enhance our understanding of the molecular events occurring in psoriasis, and these candidate genes and pathways together may prove to be therapeutic targets for psoriasis vulgaris.
Keywords: psoriasis; psoriasis vulgaris; differentially expressed gene; hub genes; cytoscape.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Decoding Psoriasis: Integrated Bioinformatics Approach to Understand Hub Genes and Involved Pathways.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(29):3619-3630. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200311130133. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32160841
-
Identification of Novel Hub Genes Associated with Psoriasis Using Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 4;23(23):15286. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315286. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499614 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatic analysis of differentially expressed genes and signaling pathways in plaque psoriasis.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jul;20(1):225-235. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10241. Epub 2019 May 15. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31115544 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis reveals potential crosstalk genes and molecular mechanisms between ulcerative colitis and psoriasis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Dec 14;317(1):118. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03617-6. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39673621
-
Screening of Skin Lesion-Associated Genes in Patients with Psoriasis by Meta-Integration Analysis.Dermatology. 2017;233(4):277-288. doi: 10.1159/000481619. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Dermatology. 2017. PMID: 29136636 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-occurrence of endometriosis with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Genetic insights (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2025 Jul 10;30(3):171. doi: 10.3892/etm.2025.12921. eCollection 2025 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2025. PMID: 40718089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation modulates intercellular adhesion and mechanotransduction in human epidermis via ROCK2.iScience. 2023 Feb 14;26(3):106195. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106195. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36890793 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone I Ameliorates Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis by Suppressing Inflammation and Regulating Keratinocyte Differentiation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 24;19:539-552. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S504485. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39876988 Free PMC article.
-
WTAP mediated m6A-modified circ_0056856 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of IL-22-stimulated human keratinocyte by miR-197-3p/CDK1 axis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 May 24;316(6):208. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03097-8. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38787443
-
Identification of biomarkers and exploration of mechanisms for atopic dermatitis based on transcriptome and scRNA-seq data analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 4;104(27):e42291. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042291. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40629565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Psoriasis Day: International Federation of Psoriasis Associations - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

