EpCAM is essential for maintenance of the small intestinal epithelium architecture via regulation of the expression and localization of proteins that compose adherens junctions
- PMID: 33416101
- PMCID: PMC7797445
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4815
EpCAM is essential for maintenance of the small intestinal epithelium architecture via regulation of the expression and localization of proteins that compose adherens junctions
Abstract
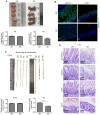
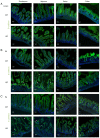
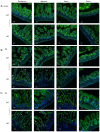
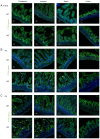
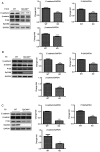
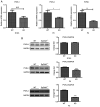
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is highly expressed in mammalian intestines, and is essential for maintaining the homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium. EpCAM protein is localized at tight junctions and the basolateral membrane of the intestinal epithelium, where it interacts with many cell adhesion molecules. To explore the molecular functions of EpCAM in regulating adherens junctions in the intestinal epithelium, EpCAM knockout embryos and newborn pups were analyzed. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was used to assess the histology of the duodenum, jejunum, ileum and colon from wild-type and EpCAM‑/‑ mice at E18.5, P0 and P3. The expression and localization of adherens junction‑associated genes and genes that encode the proteins that participate in the assembly of adherens junctions were measured at the mRNA and protein levels using qPCR, western blot analysis and immunofluorescence staining. The results showed that although there was no significant damage to the intestines of EpCAM‑/‑ mice at E18.5 and P0, they were significantly damaged at P3 in mutant mice. The expression of adherens junction‑associated genes in EpCAM mutant mice was normal at the mRNA level from E18.5 to P3, but their protein levels were gradually reduced and mislocalized from E18.5 to P3. The expression of nectin 1, which can regulate the assembly and adhesion activity of E‑cadherin, was also gradually reduced at both the mRNA and protein levels in the intestinal epithelium of EpCAM mutant mice from E18.5 to P3. In summary, the loss of EpCAM may cause the reduction and mislocalization of proteins that compose adherens junctions partly via the downregulation of nectin 1 in the intestines.
Keywords: EpCAM; intestinal epithelium; adherens junction; nectin 1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EpCAM Is Essential to Maintaining the Immune Homeostasis of Intestines via Keeping the Expression of pIgR in the Intestinal Epithelium of Mice.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 13;13:843378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.843378. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35493520 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ablation of afadin causes mislocalization and deformation of Paneth cells in the mouse small intestinal epithelium.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 21;9(10):e110549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110549. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25333284 Free PMC article.
-
EpCAM contributes to formation of functional tight junction in the intestinal epithelium by recruiting claudin proteins.Dev Biol. 2012 Nov 15;371(2):136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22819673
-
Shedding light on the EpCAM: An overview.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):12569-12580. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28132. Epub 2019 Jan 9. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30628064 Review.
-
Immunoglobulin superfamily receptors and adherens junctions.Subcell Biochem. 2012;60:137-70. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4186-7_7. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22674071 Review.
Cited by
-
Early-onset tufting enteropathy in HAI-2-deficient mice is independent of matriptase-mediated cleavage of EpCAM.Development. 2023 Sep 1;150(17):dev201801. doi: 10.1242/dev.201801. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Development. 2023. PMID: 37539662 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of RKIP in the Regulation of EMT in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;14(19):4596. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194596. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limosilactobacillus reuteri SLZX19-12 Protects the Colon from Infection by Enhancing Stability of the Gut Microbiota and Barrier Integrity and Reducing Inflammation.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0212421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02124-21. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35658572 Free PMC article.
-
The role of N-glycosylation modification in the pathogenesis of liver cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Mar 29;14(3):222. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05733-z. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36990999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocol for the establishment and characterization of South African patient-derived intestinal organoids.STAR Protoc. 2025 Jul 22;6(3):103970. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.103970. Online ahead of print. STAR Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40705597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slanchev K, Carney TJ, Stemmler MP, Koschorz B, Amsterdam A, Schwarz H, Hammerschmidt M. The epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM is required for epithelial morphogenesis and integrity during zebrafish epiboly and skin development. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000563. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

