Discriminating subcortical ischemic vascular disease and Alzheimer's disease by diffusion kurtosis imaging in segregated thalamic regions
- PMID: 33416206
- PMCID: PMC8046043
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25342
Discriminating subcortical ischemic vascular disease and Alzheimer's disease by diffusion kurtosis imaging in segregated thalamic regions
Abstract
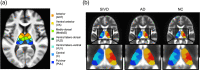
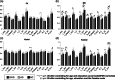
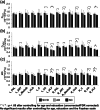
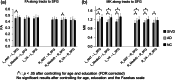
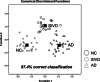
Differentiating between subcortical ischemic vascular disease (SIVD), Alzheimer's disease (AD), and normal cognition (NC) remains a challenge, and reliable neuroimaging biomarkers are needed. The current study, therefore, investigated the discriminative ability of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) metrics in segregated thalamic regions and compare with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics. Twenty-three SIVD patients, 30 AD patients, and 24 NC participants underwent brain magnetic resonance imaging. The DKI metrics including mean kurtosis (MK), axial kurtosis (Kaxial ) and radial kurtosis (Kradial ) and the DTI metrics including diffusivity and fractional anisotropy (FA) were measured within the whole thalamus and segregated thalamic subregions. Strategic correlations by group, thalamo-frontal connectivity, and canonical discriminant analysis (CDA) were used to demonstrate the discriminative ability of DKI for SIVD, AD, and NC. Whole and segregated thalamus analysis suggested that DKI metrics are less affected by white matter hyperintensities compared to DTI metrics. Segregated thalamic analysis showed that MK and Kradial were notably different between SIVD and AD/NC. The correlation analysis between Kaxial and MK showed a nonsignificant relationship in SIVD group, a trend of negative relationship in AD group, and a significant positive relationship in NC group. A wider spatial distribution of thalamo-frontal connectivity differences across groups was shown by MK compared to FA. CDA showed a discriminant power of 97.4% correct classification using all DKI metrics. Our findings support that DKI metrics could be more sensitive than DTI metrics to reflect microstructural changes within the gray matter, hence providing complementary information for currently outlined pathogenesis of SIVD and AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; canonical discriminant analysis; dementia; diffusion kurtosis imaging; diffusion tensor imaging; subcortical ischemic vascular disease; thalamus.
© 2021 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Joint diffusional kurtosis magnetic resonance imaging analysis of white matter and the thalamus to identify subcortical ischemic vascular disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 31;14(1):2570. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52910-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38297073 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of diffusion tensor imaging in differentiating early-stage subcortical ischemic vascular disease, Alzheimer's disease and normal ageing.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 7;12(4):e0175143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175143. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28388630 Free PMC article.
-
The value of diffusion tensor imaging in the differential diagnosis of subcortical ischemic vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease in patients with only mild white matter alterations on T2-weighted images.Acta Radiol. 2012 Apr 1;53(3):312-7. doi: 10.1258/ar.2011.110272. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Acta Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22416261
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
-
Advances in The Application and Research of Magnetic Resonance Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in The Musculoskeletal System.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023 Mar;57(3):670-689. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28463. Epub 2022 Oct 6. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36200754 Review.
Cited by
-
Dissociable Functional Brain Networks Associated With Apathy in Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease and Alzheimer's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Feb 3;13:717037. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.717037. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35185511 Free PMC article.
-
Study of gray matter atrophy pattern with subcortical ischemic vascular disease-vascular cognitive impairment no dementia based on structural magnetic resonance imaging.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Feb 6;15:1051177. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1051177. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36815175 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: White matter hyperintensities: the messages beneath and beyond.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jan 19;16:1367024. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1367024. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38313437 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 14;22(10):5216. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105216. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34069159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joint diffusional kurtosis magnetic resonance imaging analysis of white matter and the thalamus to identify subcortical ischemic vascular disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 31;14(1):2570. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52910-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38297073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Battistella, G. , Najdenovska, E. , Maeder, P. , Ghazaleh, N. , Daducci, A. , Thiran, J. P. , … Fornari, E. (2017). Robust thalamic nuclei segmentation method based on local diffusion magnetic resonance properties. Brain Structure & Function, 222(5), 2203–2216. 10.1007/s00429-016-1336-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini, Y. , & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300.
-
- Cox, R. W. (1996). AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Computers and Biomedical Research, 29(3), 162–173. - PubMed
-
- Erkinjuntti, T. , Inzitari, D. , Pantoni, L. , Wallin, A. , Scheltens, P. , Rockwood, K. , … Desmond, D. W. (2000). Research criteria for subcortical vascular dementia in clinical trials. In Advances in Dementia Research (pp. 23–30). Vienna, Austria: Springer. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

