Methotrexate attenuates vascular inflammation through an adenosine-microRNA-dependent pathway
- PMID: 33416495
- PMCID: PMC7840179
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.58064
Methotrexate attenuates vascular inflammation through an adenosine-microRNA-dependent pathway
Abstract
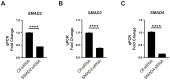
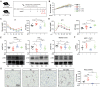
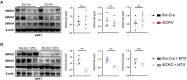
Endothelial cell (EC) activation is an early hallmark in the pathogenesis of chronic vascular diseases. MicroRNA-181b (Mir181b) is an important anti-inflammatory mediator in the vascular endothelium affecting endotoxemia, atherosclerosis, and insulin resistance. Herein, we identify that the drug methotrexate (MTX) and its downstream metabolite adenosine exert anti-inflammatory effects in the vascular endothelium by targeting and activating Mir181b expression. Both systemic and endothelial-specific Mir181a2b2-deficient mice develop vascular inflammation, white adipose tissue (WAT) inflammation, and insulin resistance in a diet-induced obesity model. Moreover, MTX attenuated diet-induced WAT inflammation, insulin resistance, and EC activation in a Mir181a2b2-dependent manner. Mechanistically, MTX attenuated cytokine-induced EC activation through a unique adenosine-adenosine receptor A3-SMAD3/4-Mir181b signaling cascade. These findings establish an essential role of endothelial Mir181b in controlling vascular inflammation and that restoring Mir181b in ECs by high-dose MTX or adenosine signaling may provide a potential therapeutic opportunity for anti-inflammatory therapy.
Keywords: adenosine; endothelial cells; human; immunology; inflammation; medicine; methotrexate; microRNA; mouse.
© 2021, Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DY, SH, HZ, DP, XS, LC, JL, JH, TY, IH, MF No competing interests declared
Figures











References
-
- Chan ES, Cronstein BN. Mechanisms of action of methotrexate. Bulletin of the Hospital for Joint Disease. 2013;71:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Charles-Schoeman C, Yin Lee Y, Shahbazian A, Wang X, Elashoff D, Curtis JR, Navarro-Millán I, Yang S, Chen L, Cofield SS, Moreland LW, Paulus H, O'Dell J, Bathon J, Louis Bridges S, Reddy ST. Improvement of High-Density lipoprotein function in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate monotherapy or combination therapies in a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 2017;69:46–57. doi: 10.1002/art.39833. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

