Are all cytokine storms the same?
- PMID: 33416946
- PMCID: PMC7791954
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-020-02822-2
Are all cytokine storms the same?
Abstract
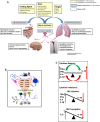
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is the result of massive pro-inflammatory cytokine release and imbalance in the absence of adequate immunomodulation from signals such as interleukin (IL)-10, resulting in ongoing inflammation, tissue damage and death if left uncontrolled. Although CRS can result from different pro-inflammatory insults, the treatments proposed are similar, regardless of the phase of response. SARS-CoV-2 causes COVID-19, and CRS has been a defining feature of severe disease. Common approaches to treating CRS in other conditions are now applied to COVID-19 and, although some patients respond, it begs the following questions: (1) are all cytokine storms the same regardless of initiating insult, (2) can treatments be considered equally for all CRS events at any phase of the response, (3) can CRS be predicted based on dynamic acute biomarkers and, (4) should patients with CRS undergo long-term monitoring for secondary effects? The aim of this commentary is not to provide a review of COVID-19 pathophysiology or of cytokine storm, but rather to establish a foundation which could act as a platform to inform treatment approaches to CRS, regardless of cause, and the short- and long-term follow-up which may be necessary for affected patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; CRS; Cytokine release syndrome; Cytokine storm; SARS-CoV-2; TGN1412.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Teachey DT, Lacey SF, Shaw PA, Melenhorst JJ, Maude SL, Frey N, et al. Identification of predictive biomarkers for cytokine release syndrome after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:664–679. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

