Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Persistent Viral Shedding in Hospitalized Adult Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 33417230
- PMCID: PMC7791162
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-020-00381-8
Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Persistent Viral Shedding in Hospitalized Adult Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background: The goal of this study was to investigate the prevalence and factors associated with persistent viral shedding (PVS) in hospitalized patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection.
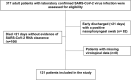
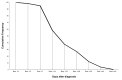
Methods: This was a prospective observational study including all consecutive adults hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection. When the first nasopharyngeal swab was positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA (day 0), additional samples were obtained on days + 3, + 5, + 7 and then once every 7 days until virus detection was negative. PVS was defined as the duration of shedding of at least 21 days after diagnosis. The primary endpoint of this study was the prevalence of PVS.
Results: Data were obtained regarding 121 consecutive hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection (median age 66 years, male sex 65.3%). Overall, the prevalence of PVS was 38% (46/121 patients). According to univariate analysis, factors associated with PVS were immunosuppression (6.7% vs 21.7%, p = 0.02), increased interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels (≥ 35 ng/ml) at the time of diagnosis (43.4% vs 67.3%, p = 0.02), time from onset of symptoms to diagnosis (median days 7.0 vs 3.5, p = 0.001), intensive care unit admission (22.7% vs 43.5%, p = 0.02), and need for invasive mechanical ventilation (20.0% vs 41.3%, p = 0.01). The multivariate analysis indicated that immunosuppression, increased IL-6 levels at the time of diagnosis, time from onset of symptoms to diagnosis, and need for mechanical ventilation were independent factors associated with PVS.
Conclusions: PVS was detected in up to 38% of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection and was strongly associated with immunosuppression, increased IL-6 levels, and the need for mechanical ventilation.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6; Outcome; SARS-CoV-2; Viral shedding.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous