A systematic review to examine the relationship between objective and patient-reported outcome measures in sinonasal disorders: recommendations for use in research and clinical practice
- PMID: 33417297
- PMCID: PMC8248036
- DOI: 10.1002/alr.22744
A systematic review to examine the relationship between objective and patient-reported outcome measures in sinonasal disorders: recommendations for use in research and clinical practice
Abstract
Background: Common sinonasal disorders include chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), allergic rhinitis (AR), and a deviated nasal septum (DNS), which often coexist with shared common symptoms including nasal obstruction, olfactory dysfunction, and rhinorrhea. Various objective outcome measures and patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) are used to assess disease severity; however, there is limited evidence in the literature on the correlation between them. This systematic review aims to examine the relationship between them and provide recommendations.
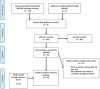
Methods: A search of MEDLINE and EMBASE identified studies quantifying correlations between objective outcome measures and PROMs for the sinonasal conditions using a narrative synthesis.
Results: In total, 59 studies met inclusion criteria. For nasal obstruction, rhinomanometry shows a lack of correlation whereas peak nasal inspiratory flow (PNIF) shows the strongest correlation with PROMs (r > 0.5). The Sniffin' Stick test shows a stronger correlation with PROMs (r > 0.5) than the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test (UPSIT) (r < 0.5). Computed tomography (CT) sinus scores show little evidence of correlation with PROMs and nasal endoscopic ratings (weak correlation, r < 0.5).
Conclusion: Overall, objective outcome measures and PROMs assessing sinonasal symptoms are poorly correlated, and we recommend that objective outcome measures be used with validated PROMs depending on the setting. PNIF should be used in routine clinical practice for nasal obstruction; rhinomanometry and acoustic rhinometry may be useful in research. The Sniffin' Sticks test is recommended for olfactory dysfunction with UPSIT as an alternative. CT scores should be excluded as a routine CRS outcome measure, and endoscopic scores should be used in combination with PROMs until further research is conducted.
Keywords: SNOT-22; allergic rhinitis; chronic rhinosinusitis; mucociliary clearance; olfactory test; patient-reported outcome measures; rhinitis.
© 2020 The Authors. International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Academy of Otolaryngic Allergy and American Rhinologic Society.
Figures
References
-
- Hastan D, Fokkens WJ, Bachert C, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis in Europe—an underestimated disease. A GA(2)LEN study. Allergy. 2011;66:1216‐1223. - PubMed
-
- Gliklich RE, Metson R. The health impact of chronic sinusitis in patients seeking otolaryngologic care. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995;113:104‐109. - PubMed
-
- Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Quantification for staging sinusitis. The Staging and Therapy Group. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1995;167:17‐21. - PubMed
-
- Lildholdt T, Rundcrantz H, Lindqvist N. Efficacy of topical corticosteroid powder for nasal polyps: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of budesonide. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1995;20:26‐30. - PubMed
-
- Kupferberg SB, Bent JP 3rd, Kuhn FA. Prognosis for allergic fungal sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997;117:35‐41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous