Biomolecular Condensates and Cancer
- PMID: 33417833
- PMCID: PMC8721577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.12.003
Biomolecular Condensates and Cancer
Abstract
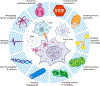
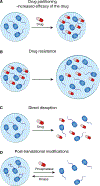
Malignant transformation is characterized by dysregulation of diverse cellular processes that have been the subject of detailed genetic, biochemical, and structural studies, but only recently has evidence emerged that many of these processes occur in the context of biomolecular condensates. Condensates are membrane-less bodies, often formed by liquid-liquid phase separation, that compartmentalize protein and RNA molecules with related functions. New insights from condensate studies portend a profound transformation in our understanding of cellular dysregulation in cancer. Here we summarize key features of biomolecular condensates, note where they have been implicated-or will likely be implicated-in oncogenesis, describe evidence that the pharmacodynamics of cancer therapeutics can be greatly influenced by condensates, and discuss some of the questions that must be addressed to further advance our understanding and treatment of cancer.
Keywords: biomolecular condensates; cancer; cancer therapeutics; dysregulated state; intrinsically disordered protein; phase separation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
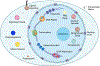
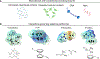
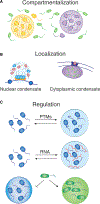
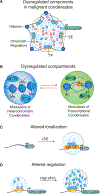
References
-
- Alberti S. (2017). The wisdom of crowds: regulating cell function through condensed states of living matter. J. Cell Sci. 130, 2789–2796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

