Uptake of and factors associated with testing for sexually transmitted infections in community-based settings among youth in Zimbabwe: a mixed-methods study
- PMID: 33417838
- PMCID: PMC7818532
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30335-7
Uptake of and factors associated with testing for sexually transmitted infections in community-based settings among youth in Zimbabwe: a mixed-methods study
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) among youth is high in sub-Saharan Africa. We investigated the uptake of testing for and prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis (chlamydia) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhoea) infections among youth in community-based settings in Zimbabwe, and explored the facilitators and barriers to testing.
Methods: This study was nested within a cluster randomised trial of community-based delivery of integrated HIV and sexual and reproductive health services for youth aged 16-24 years. Chlamydia and gonorrhoea testing via urine samples using the Xpert CT/NG test was offered in the four intervention clusters in Harare, Zimbabwe. Factors associated with testing uptake were investigated in a subset of participants (n=257) using hierarchical multivariate logistic regression. In-depth interviews with a separate purposively selected sample (n=26) explored facilitators and barriers to STI testing and partner notification and were analysed using thematic analysis.
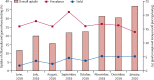
Findings: Between June 1, 2019, and Jan 31, 2020, there were 6200 attendances by 4440 participants (78·2% women, 21·8% men) median age 20·3 (IQR 17·9-22·8) years. 1478 participants had 1501 tests done, and 248 tests were positive and 1253 tests were negative for chlamydia or gonorrhoea, or both. STI test uptake was 33·3% (95% CI 31·9-34·7), increasing from 11·7% in June, 2019, to 37·1% in January, 2020. The prevalence of chlamydia or gonorrhoea, or both, was 16·5% (95% CI 14·7-18·5; 248 of 1501), with only seven participants (3%) showing symptoms. The overall yield of testing was 4·0% (95% CI 3·5-4·5; 248 of 6200). Uptake was associated with having symptoms (adjusted odds ratio [OR] 14·8, 95% CI 1·66-132·07) and negatively associated with being single (adjusted OR 0·33, 95% CI 0·13-0·84) or having a boyfriend or girlfriend (adjusted OR 0·19, 95% CI 0·087-0·43) compared with being married, and being a student compared with being employed (adjusted OR 0·26, 95% CI 0·10-0·68). Perceived risk and symptoms of STIs were motivators for testing whereas misinformation, anticipated stigma, and concern about confidentiality were barriers.
Interpretation: The prevalence of chlamydia or gonorrhoea, or both, was high among youth but only a minority were symptomatic. Therefore most infections would remain untreated without access to STI testing. Provision of education, counselling, and confidentiality are essential to improve uptake and acceptability of STI testing.
Funding: Wellcome Trust.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Testing for sexually transmitted infections among youth in Zimbabwe.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021 Feb;5(2):93-94. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30394-1. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021. PMID: 33417837 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2019. Progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections 2019. Accountability for the global health sector strategies, 2016–2021.
-
- Barnabas SL, Dabee S, Passmore JS. Converging epidemics of sexually transmitted infections and bacterial vaginosis in southern African female adolescents at risk of HIV. Int J STD AIDS. 2018;29:531–539. - PubMed
-
- Sarkodie F, Ullum H, Owusu-Dabo E, Owusu-Ofori S, Owusu-Ofori A, Hassall O. A novel strategy for screening blood donors for syphilis at Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital, Ghana. Transfus Med. 2016;26:63–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical