One health therapeutics: Target-Based drug development for cryptosporidiosis and other apicomplexa diseases
- PMID: 33418437
- PMCID: PMC8582285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2020.109336
One health therapeutics: Target-Based drug development for cryptosporidiosis and other apicomplexa diseases
Abstract
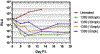
This is a review of the development of bumped-kinase inhibitors (BKIs) for the therapy of One Health parasitic apicomplexan diseases. Many apicomplexan infections are shared between humans and livestock, such as cryptosporidiosis and toxoplasmosis, as well as livestock only diseases such as neosporosis. We have demonstrated proof-of-concept for BKI therapy in livestock models of cryptosporidiosis (newborn calves infected with Cryptosporidium parvum), toxoplasmosis (pregnant sheep infected with Toxoplasma gondii), and neosporosis (pregnant sheep infected with Neospora caninum). We discuss the potential uses of BKIs for the treatment of diseases caused by apicomplexan parasites in animals and humans, and the improvements that need to be made to further develop BKIs.
Keywords: Antiparastics; Apicomplexa; Kinase inhibitors.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
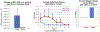
References
-
- Amadi B, Mwiya M, Musuku J, Watuka A, Sianongo S, Ayoub A, Kelly P, 2002. Effect of nitazoxanide on morbidity and mortality in Zambian children with cryptosporidiosis: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 360, 1375–1380. - PubMed
-
- Arnold SLM, Choi R, Hulverson MA, Schaefer DA, Vinayak S, Vidadala RSR, McCloskey MC, Whitman GR, Huang W, Barrett LK, Ojo KK, Fan E, Maly DJ, Riggs MW, Striepen B, Van Voorhis WC, 2017. Necessity of Bumped Kinase Inhibitor Gastrointestinal Exposure in Treating Cryptosporidium Infection. J Infect Dis 216, 55–63. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bishop AC, Shah K, Liu Y, Witucki L, Kung C, Shokat KM, 1998. Design of allele-specific inhibitors to probe protein kinase signaling. Curr Biol 8, 257–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

