E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: Key Regulators of TGFβ Signaling in Cancer Progression
- PMID: 33418880
- PMCID: PMC7825147
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020476
E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: Key Regulators of TGFβ Signaling in Cancer Progression
Abstract
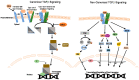
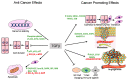
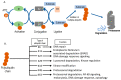
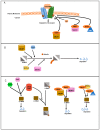
Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) is a secreted growth and differentiation factor that influences vital cellular processes like proliferation, adhesion, motility, and apoptosis. Regulation of the TGFβ signaling pathway is of key importance to maintain tissue homeostasis. Perturbation of this signaling pathway has been implicated in a plethora of diseases, including cancer. The effect of TGFβ is dependent on cellular context, and TGFβ can perform both anti- and pro-oncogenic roles. TGFβ acts by binding to specific cell surface TGFβ type I and type II transmembrane receptors that are endowed with serine/threonine kinase activity. Upon ligand-induced receptor phosphorylation, SMAD proteins and other intracellular effectors become activated and mediate biological responses. The levels, localization, and function of TGFβ signaling mediators, regulators, and effectors are highly dynamic and regulated by a myriad of post-translational modifications. One such crucial modification is ubiquitination. The ubiquitin modification is also a mechanism by which crosstalk with other signaling pathways is achieved. Crucial effector components of the ubiquitination cascade include the very diverse family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. This review summarizes the diverse roles of E3 ligases that act on TGFβ receptor and intracellular signaling components. E3 ligases regulate TGFβ signaling both positively and negatively by regulating degradation of receptors and various signaling intermediates. We also highlight the function of E3 ligases in connection with TGFβ's dual role during tumorigenesis. We conclude with a perspective on the emerging possibility of defining E3 ligases as drug targets and how they may be used to selectively target TGFβ-induced pro-oncogenic responses.
Keywords: E3 Ligase; PROTAC; SMAD; SMURF; TGFβ; cancer; signaling; tumor; ubiquitin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Key role for ubiquitin protein modification in TGFβ signal transduction.Ups J Med Sci. 2012 May;117(2):153-65. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2012.654858. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Ups J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22335355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of TGF-beta family signaling by E3 ubiquitin ligases.Cancer Sci. 2008 Nov;99(11):2107-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00925.x. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18808420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase PJA1 Enhances Tumor-Suppressing TGFβ Signaling.Cancer Res. 2020 May 1;80(9):1819-1832. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3116. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32127355 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of TGFbeta signaling in cancer.Neoplasia. 2006 Aug;8(8):677-88. doi: 10.1593/neo.06472. Neoplasia. 2006. PMID: 16925950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Itch E3 ubiquitin ligase positively regulates TGF-β signaling to EMT via Smad7 ubiquitination.Mol Cells. 2015 Jan 31;38(1):20-5. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2015.2120. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Mol Cells. 2015. PMID: 25518932 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transforming Growth Factor-β: An Agent of Change in the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 12;9:764727. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.764727. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34712672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of transforming growth factor-β signaling as a therapeutic approach to treating colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 7;28(33):4744-4761. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i33.4744. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36156927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-30c-5p loss-induced PELI1 accumulation regulates cell proliferation and migration via activating PI3K/AKT pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2022 Jan 6;20(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03226-1. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 34991623 Free PMC article.
-
Control of TGFβ signalling by ubiquitination independent function of E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIP12.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Oct 20;14(10):692. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06215-y. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37863914 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered extracellular vesicle-encapsulated CHIP as novel nanotherapeutics for treatment of renal fibrosis.NPJ Regen Med. 2024 Jan 13;9(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41536-024-00348-0. NPJ Regen Med. 2024. PMID: 38218925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inagaki M., Moustakas A., Lin H.Y., Lodish H.F., Carr B.I. Growth inhibition by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) type I is restored in TGF-β-resistant hepatoma cells after expression of TGF-beta receptor type II cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1993;90:5359–5363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5359. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

