Flavonoids: Nutraceuticals for Rheumatic Diseases via Targeting of Inflammasome Activation
- PMID: 33418975
- PMCID: PMC7825303
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020488
Flavonoids: Nutraceuticals for Rheumatic Diseases via Targeting of Inflammasome Activation
Abstract
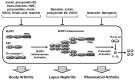
Inflammation, an innate immune response that prevents cellular damage caused by pathogens, consists of two successive mechanisms, namely priming and triggering. While priming is an inflammation-preparation step, triggering is an inflammation-activation step, and the central feature of triggering is the activation of inflammasomes and intracellular inflammatory protein complexes. Flavonoids are natural phenolic compounds predominantly present in plants, fruits, and vegetables and are known to possess strong anti-inflammatory activities. The anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids has long been demonstrated, with the main focus on the priming mechanisms, while increasing numbers of recent studies have redirected the research focus on the triggering step, and studies have reported that flavonoids inhibit inflammatory responses and diseases by targeting inflammasome activation. Rheumatic diseases are systemic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases that primarily affect joints and connective tissues, and they are associated with numerous deleterious effects. Here, we discuss the emerging literature on the ameliorative role of flavonoids targeting inflammasome activation in inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; flavonoids; inflammasomes; nutraceuticals; rheumatic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory Roles of Flavonoids in Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammatory Responses and Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 20;24(12):10402. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210402. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural compounds flavonoids as modulators of inflammasomes in chronic diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jul;84:106498. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106498. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32304996 Review.
-
Regulatory Roles of Flavonoids on Inflammasome Activation during Inflammatory Responses.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018 Jul;62(13):e1800147. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201800147. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018. PMID: 29774640 Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of NLRP3 Inflammasomes by Natural Products and Pharmaceuticals: A Novel Mechanistic Approach for Inflammatory Diseases.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(16):1645-1670. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170227121619. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28245768 Review.
-
[Advances in mechanisms for NLRP3 inflammasomes regulation].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2016 Oct;51(10):1505-12. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 29924571 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Cardio-Rheumatic Diseases: Inflammasomes Behaving Badly.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 9;26(8):3520. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083520. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40331999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial of Special Issue "Regulatory Roles of Inflammasomes in Human Diseases".Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 16;22(6):3008. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063008. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809447 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of High-Pressure Processing on Antioxidant Activity during Storage of Fruits and Fruit Products: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Aug 30;26(17):5265. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175265. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Interplay between Methyltransferases and Inflammasomes in Inflammatory Responses and Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 15;22(14):7580. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147580. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Roles of Flavonoids in Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammatory Responses and Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 20;24(12):10402. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210402. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

