tRNA Biology in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes: Role of Genetic and Environmental Factors
- PMID: 33419045
- PMCID: PMC7825315
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020496
tRNA Biology in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes: Role of Genetic and Environmental Factors
Abstract
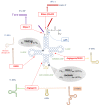
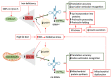
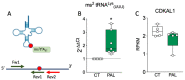
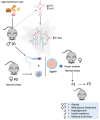
The global rise in type 2 diabetes results from a combination of genetic predisposition with environmental assaults that negatively affect insulin action in peripheral tissues and impair pancreatic β-cell function and survival. Nongenetic heritability of metabolic traits may be an important contributor to the diabetes epidemic. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are noncoding RNA molecules that play a crucial role in protein synthesis. tRNAs also have noncanonical functions through which they control a variety of biological processes. Genetic and environmental effects on tRNAs have emerged as novel contributors to the pathogenesis of diabetes. Indeed, altered tRNA aminoacylation, modification, and fragmentation are associated with β-cell failure, obesity, and insulin resistance. Moreover, diet-induced tRNA fragments have been linked with intergenerational inheritance of metabolic traits. Here, we provide a comprehensive review of how perturbations in tRNA biology play a role in the pathogenesis of monogenic and type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: insulin resistance; obesity; pancreatic β-cells; tRNA; tRNA fragments; tRNA modifications; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare to have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The tRNA Epitranscriptome and Diabetes: Emergence of tRNA Hypomodifications as a Cause of Pancreatic β-Cell Failure.Endocrinology. 2019 May 1;160(5):1262-1274. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00098. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30907926 Review.
-
The occurrence order and cross-talk of different tRNA modifications.Sci China Life Sci. 2021 Sep;64(9):1423-1436. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1906-4. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Sci China Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33881742 Review.
-
The tRNA-associated dysregulation in diabetes mellitus.Metabolism. 2019 May;94:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.01.017. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Metabolism. 2019. PMID: 30711570 Review.
-
Transfer RNAs: diversity in form and function.RNA Biol. 2021 Mar;18(3):316-339. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1809197. Epub 2020 Sep 9. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32900285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The landscape of Arabidopsis tRNA aminoacylation.Plant J. 2024 Dec;120(6):2784-2802. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17146. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 39555621 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Skeletal muscle cystathionine γ-lyase deficiency promotes obesity and insulin resistance and results in hyperglycemia and skeletal muscle injury upon HFD in mice.Redox Rep. 2024 Dec;29(1):2347139. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2024.2347139. Epub 2024 May 8. Redox Rep. 2024. PMID: 38718286 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation and Diversification of tRNA t6A-Modifying Enzymes across the Three Domains of Life.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 6;23(21):13600. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113600. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Epitranscriptomics in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 27;13:907060. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.907060. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35692393 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid intake, plasma metabolites, and incident type 2 diabetes risk: a systematic approach in prospective cohort studies.Nutr J. 2025 Jul 16;24(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12937-025-01157-x. Nutr J. 2025. PMID: 40671038 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Metabolic Biomarkers of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 in Aged Adults Determined by a UPLC-MS Metabolomic Approach.Metabolites. 2025 Jun 12;15(6):395. doi: 10.3390/metabo15060395. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40559420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xue A., eQTLGen Consortium. Wu Y., Zhu Z., Zhang F., Kemper K.E., Zheng Z., Yengo L., Lloyd-Jones L.R., Sidorenko J., et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 143 risk variants and putative regulatory mechanisms for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04951-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cersosimo E., Triplitt C., Solis-Herrera C., Mandarino L.J., DeFronzo R.A. In: Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Feingold K.R., Anawalt B., Boyce A., Chrousos G., de Herder W.W., Dungan K., Grossman A., Hershman J.M., Hofland H.J., Kaltsas G., editors. Endotext [Internet]; South Dartmouth, MA, USA: 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- --/Fonds De La Recherche Scientifique - FNRS
- -/Brussels Region Innoviris project DiaType
- grant agreement No 115881/Fonds Erasme for Medical Research and the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking Rhapsody
- -/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, EFPIA
- under contract number 16.009.7/Swiss State Secretariat for Education' Research and Innovation (SERI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

