Annexin 1 Is a Component of eATP-Induced Cytosolic Calcium Elevation in Arabidopsis thaliana Roots
- PMID: 33419052
- PMCID: PMC7825420
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020494
Annexin 1 Is a Component of eATP-Induced Cytosolic Calcium Elevation in Arabidopsis thaliana Roots
Abstract
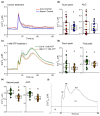
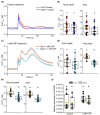
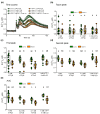
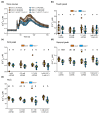
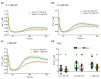
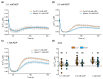
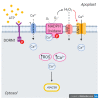
Extracellular ATP (eATP) has long been established in animals as an important signalling molecule but this is less understood in plants. The identification of Arabidopsis thaliana DORN1 (Does Not Respond to Nucleotides) as the first plant eATP receptor has shown that it is fundamental to the elevation of cytosolic free Ca2+ ([Ca2+]cyt) as a possible second messenger. eATP causes other downstream responses such as increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide, plus changes in gene expression. The plasma membrane Ca2+ influx channels involved in eATP-induced [Ca2+]cyt increase remain unknown at the genetic level. Arabidopsis thaliana Annexin 1 has been found to mediate ROS-activated Ca2+ influx in root epidermis, consistent with its operating as a transport pathway. In this study, the loss of function Annexin 1 mutant was found to have impaired [Ca2+]cyt elevation in roots in response to eATP or eADP. Additionally, this annexin was implicated in modulating eATP-induced intracellular ROS accumulation in roots as well as expression of eATP-responsive genes.
Keywords: ADP; Arabidopsis; annexin 1; calcium; calcium channel; extracellular ATP; reactive oxygen species; root.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
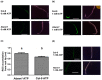
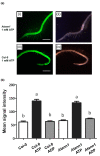
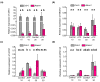
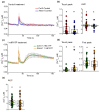
References
-
- Clark G., Torres J., Herz N., Wat N., Ogoti J., Aranda G., Blizard M., Wu M., Onyirimba J., Canales A.A., et al. Both the stimulation and inhibition of root hair growth induced by extracellular nucleotides in Arabidopsis are mediated by nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010;74:423–435. doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9683-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

