Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Indices, Duodenal Histomorphology, and Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens Fed on Diets Supplemented with Cinnamon Bark Powder at Prestarter and Starter Phases
- PMID: 33419092
- PMCID: PMC7825433
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11010094
Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Indices, Duodenal Histomorphology, and Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens Fed on Diets Supplemented with Cinnamon Bark Powder at Prestarter and Starter Phases
Abstract
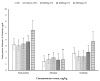
Ross 308 broiler chicks (n = 240) aged 1 day were assigned to five groups for eight replicates (six chicks for each) (3♂ and 3♀). Basal dietary groups were supplemented by 2000, 4000, and 6000 mg/kg cinnamon (CN) for 21 days. Basal diet alone was used as a negative control, and basal antibiotic diet (Colimox) was used as a positive control. At 10, 14, and 21 days of age, chicks that received 2000 mg CN and Colimox had a higher body weight, resulting in an increase in body weight gain. CN also resulted in the maximum improvement in the feed conversion ratio and feed efficiency over 1-21 days at the level of 2000 mg/kg. At days 10, the maximum relative breast weight was 2000 mg/kg of CN. Mean serum albumin concentrations, duodenal villus height, and goblet cell density increased (p < 0.05) by 2000 mg/kg of CN, and mean serum globulin and total protein concentrations and crypt depth increased (p < 0.05) by 6000 mg/kg of CN compared with control. Increased cecal Escherichia coli number was CN dose-dependent. In conclusion, dietary inclusion of 2000 mg/kg CN can be applied as an alternative to in-feed antibiotics for broiler starter diet.
Keywords: broiler chicks; cinnamon; goblet cell; growth promoter; triiodothyronine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors hereby declare that no conflict or competing of interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014.
-
- Leeson S. Predictions for Commercial Poultry Nutrition. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2008;17:315–322. doi: 10.3382/japr.2007-00101. - DOI
-
- European Medicines Agency . Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 30 European Countries in 2015. European Medicines Agency; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2017. p. 178.
-
- Hughes P., Heritage J. Antibiotic growth-promoters in food animals. FAO Anim. Prod. Health. 2004;160:129–152.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

