Microneedle Arrays Combined with Nanomedicine Approaches for Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutics
- PMID: 33419118
- PMCID: PMC7825522
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10020181
Microneedle Arrays Combined with Nanomedicine Approaches for Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutics
Abstract
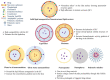
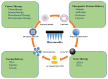
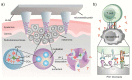
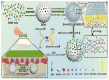
Organic and inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) have shown promising outcomes in transdermal drug delivery. NPs can not only enhance the skin penetration of small/biomacromolecule therapeutic agents but can also impart control over drug release or target impaired tissue. Thanks to their unique optical, photothermal, and superparamagnetic features, NPs have been also utilized for the treatment of skin disorders, imaging, and biosensing applications. Despite the widespread transdermal applications of NPs, their delivery across the stratum corneum, which is the main skin barrier, has remained challenging. Microneedle array (MN) technology has recently revealed promising outcomes in the delivery of various formulations, especially NPs to deliver both hydrophilic and hydrophobic therapeutic agents. The present work reviews the advancements in the application of MNs and NPs for an effective transdermal delivery of a wide range of therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy, photothermal and photodynamic therapy, peptide/protein vaccination, and the gene therapy of various diseases. In addition, this paper provides an overall insight on MNs' challenges and summarizes the recent achievements in clinical trials with future outlooks on the transdermal delivery of a wide range of nanomedicines.
Keywords: drug delivery; gene delivery; immunotherapy; microneedle arrays; nanomedicine; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Zhou X., Hao Y., Yuan L., Pradhan S., Shrestha K., Pradhan O., Liu H., Li W. Nano-formulations for transdermal drug delivery: A review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018;29:1713–1724. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2018.10.037. - DOI
-
- Moradi L., Javanmardi S., Abolmaali S., Mohammadi Samani S. Passive Enhancement of Transdermal Drug Delivery: Lipid-Based Colloidal Carriers as an Emerging Pharmaceutical Technology Platform. TiPS. 2019;5:25–40.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

