Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway Regulates ALDH and Contributes to Radioresistance in Breast Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 33419140
- PMCID: PMC7825579
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10010083
Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway Regulates ALDH and Contributes to Radioresistance in Breast Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
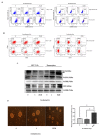
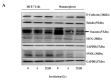
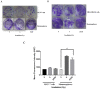
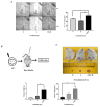
Tumor recurrence after radiotherapy due to the presence of breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) is a clinical challenge, and the mechanism remains unclear. Low levels of ROS and enhanced antioxidant defenses are shown to contribute to increasing radioresistance. However, the role of Nrf2-Keap1-Bach1 signaling in the radioresistance of BCSCs remains elusive. Fractionated radiation increased the percentage of the ALDH-expressing subpopulation and their sphere formation ability, promoted mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and enhanced radioresistance in BCSCs. Radiation activated Nrf2 via Keap1 silencing and enhanced the tumor-initiating capability of BCSCs. Furthermore, knockdown of Nrf2 suppressed ALDH+ population and stem cell markers, reduced radioresistance by decreasing clonogenicity and blocked the tumorigenic ability in immunocompromised mice. An underlying mechanism of Keap1 silencing could be via miR200a, as we observed a significant increase in its expression, and the promoter methylation of Keap1 or GSK-3β did not change. Our data demonstrate that ALDH+ BCSC population contributes to breast tumor radioresistance via the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway, and targeting this cell population with miR200a could be beneficial but warrants detailed studies. Our results support the notion that Nrf2-Keap1 signaling controls mesenchymal-epithelial plasticity, regulates tumor-initiating ability and promotes the radioresistance of BCSCs.
Keywords: ALDH activity; BCSC; Keap1; Nrf2; ROS; epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT); fractionated dose of γ radiation; miR200a; radioresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Hsp27 participates in the maintenance of breast cancer stem cells through regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and nuclear factor-κB.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Oct 24;13(5):R101. doi: 10.1186/bcr3042. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22023707 Free PMC article.
-
miR-140-5p Attenuates Hypoxia-Induced Breast Cancer Progression by Targeting Nrf2/HO-1 Axis in a Keap1-Independent Mechanism.Cells. 2021 Dec 22;11(1):12. doi: 10.3390/cells11010012. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011574 Free PMC article.
-
HER2-associated radioresistance of breast cancer stem cells isolated from HER2-negative breast cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Dec 15;18(24):6634-47. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1436. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23091114 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Nrf2 and ROS in regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition: implications for cancer metastasis and therapy.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 23;52(1):628. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10731-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40549063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the mTOR pathway in breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs): mechanisms and therapeutic potentials.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Mar 29;16(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04218-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40158191 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stem Cells and Irradiation.Cells. 2021 Mar 30;10(4):760. doi: 10.3390/cells10040760. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33808269 Free PMC article.
-
ALDHHigh Breast Cancer Stem Cells Exhibit a Mesenchymal-Senescent Hybrid Phenotype, with Elevated Metabolic and Migratory Activities.Cells. 2024 Dec 13;13(24):2059. doi: 10.3390/cells13242059. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39768151 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ROS in cancer: rationale and strategies.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Aug;23(8):583-606. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-00979-4. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38982305 Review.
-
Deciphering Common Traits of Breast and Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells and Possible Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 26;24(13):10683. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310683. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Luteolin Inhibits Breast Cancer Stemness and Enhances Chemosensitivity through the Nrf2-Mediated Pathway.Molecules. 2021 Oct 26;26(21):6452. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216452. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darby S.C., McGale P., Correa C.R., Taylor C.A., Arriagada R., Clarke M., Cutter D., Davies C., Ewertz M., Godwin J., et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10 801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378:1707–1716. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61629-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duru N., Fan M., Candas D., Menaa C., Liu H.-C., Nantajit D., Wen Y., Xiao K., Eldridge A., Chromy B.A., et al. HER2-Associated Radioresistance of Breast Cancer Stem Cells Isolated from HER2-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:6634–6647. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1436. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

