Involvements of Hyperhomocysteinemia in Neurological Disorders
- PMID: 33419180
- PMCID: PMC7825518
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11010037
Involvements of Hyperhomocysteinemia in Neurological Disorders
Abstract
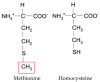
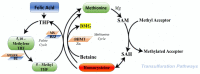
Homocysteine (HCY), a physiological amino acid formed when proteins break down, leads to a pathological condition called hyperhomocysteinemia (HHCY), when it is over a definite limit. It is well known that an increase in HCY levels in blood, can contribute to arterial damage and several cardiovascular disease, but the knowledge about the relationship between HCY and brain disorders is very poor. Recent studies demonstrated that an alteration in HCY metabolism or a deficiency in folate or vitamin B12 can cause altered methylation and/or redox potentials, that leads to a modification on calcium influx in cells, or into an accumulation in amyloid and/or tau protein involving a cascade of events that culminate in apoptosis, and, in the worst conditions, neuronal death. The present review will thus summarize how much is known about the possible role of HHCY in neurodegenerative disease.
Keywords: homocysteine; hyperhomocysteinemia; pathology; physiology; target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implication of homocysteine in protein quality control processes.Biochimie. 2019 Oct;165:19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2019.06.017. Epub 2019 Jun 30. Biochimie. 2019. PMID: 31269461 Review.
-
Mechanisms of homocysteine neurotoxicity in neurodegenerative diseases with special reference to dementia.FEBS Lett. 2006 May 29;580(13):2994-3005. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.088. Epub 2006 May 6. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16697371 Review.
-
Homocysteine and Hyperhomocysteinaemia.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(16):2948-2961. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180313105949. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29532755 Review.
-
[Review of the role of hyperhomocysteinemia and B-vitamin deficiency in neurological and psychiatric disorders--current evidence and preliminary recommendations].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2007 Sep;75(9):515-27. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-980112. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2007. PMID: 17729191 Review. German.
-
Effect of folate, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 intake and MTHFR C677T polymorphism on homocysteine concentrations of renal transplant recipients.Transplant Proc. 2007 Dec;39(10):3163-5. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.08.098. Transplant Proc. 2007. PMID: 18089344
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress impairs cognitive function by affecting hippocampal fimbria volume in drug-naïve, first-episode schizophrenia.Front Neurosci. 2023 Apr 17;17:1153439. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1153439. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37139526 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting hair breakage in alopecia areata: the central role of dysregulated cysteine homeostasis.Amino Acids. 2024 May 21;56(1):36. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03395-5. Amino Acids. 2024. PMID: 38772922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-Based Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis and Progression: An Overview.Cells. 2022 Apr 17;11(8):1367. doi: 10.3390/cells11081367. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pathophysiology of H2S in Renal Glomerular Diseases.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 26;12(2):207. doi: 10.3390/biom12020207. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2-Related Factor 2 Signaling in the Neuropathophysiology of Inherited Metabolic Disorders.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Nov 26;15:785057. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.785057. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34955754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miller A.L. The methionine-homocysteine cycle and its effects on cognitive diseases. Altern. Med. Rev. 2003;8:7–19. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins P.N., Wu L.L., Wu J., Hunt S.C., James B.C., Vincent G.M., Williams R.R. Higher plasma homocyst(e)ine and increased susceptibility to adverse effects of low folate in early familial coronary artery disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995;15:1314–1320. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.15.9.1314. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

