Impact of Plant Origin on Eurasian Propolis on Phenolic Profile and Classical Antioxidant Activity
- PMID: 33419208
- PMCID: PMC7825625
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11010068
Impact of Plant Origin on Eurasian Propolis on Phenolic Profile and Classical Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
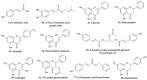
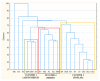
Propolis is a bee product with known medical properties, including antioxidant activity. The scope of the study is profiling 19 different Eurasian propolis samples (mostly from Russia and Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Poland, Ukraine, and Slovakia). Profiles of propolises were investigated by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-mass spectrometry (UPLC-DAD-MS). Classical antioxidant properties, which are based on electron donation mechanism, were assessed by DPPH, ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), and oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) assays. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents were also evaluated by colorimetric tests. Most of the samples exhibited significant content of polyphenols (from 30.28 to 145.24 mg GAE/g of propolis) and flavonoids (from 10.45 to 82.71 mg GAE/g of propolis). Most of the propolis samples exhibited potent antiradical (DPPH test-from 8.83 to 64.47 mg GAE/g of propolis) and reducing activity (FRAP test-from 0.08 to 1.17 mmol Fe2+/g of propolis). Based on the occurrence of marker compounds, propolis samples were classified as poplar, aspen-birch, aspen-poplar, and aspen-birch-poplar type. Main markers present in propolis of poplar (e.g., chrysin, pinocembrin, galangin, and 3-O-acetyl-pinobanksin), birch (ermanin and acacetin) and aspen (2-acetyl-1,3-di-p-coumaroylglycerol) origin were used. DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC tests results were correlated with flavonoids, total polyphenols, or the polyphenols other than flavonoids content. In term of activity, poplar propolis type was variable, while aspen-birch-poplar type usually exhibited high DPPH and FRAP activity.
Keywords: DAD; DPPH; Eurasia; FRAP; HPLC; MS; ORAC; UPLC; antioxidant; chemometry; propolis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemical Profile, Plant Precursors and Some Properties of Georgian Propolis.Molecules. 2022 Nov 9;27(22):7714. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227714. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431810 Free PMC article.
-
Main flavonoids, DPPH activity, and metal content allow determination of the geographical origin of propolis from the Province of San Juan (Argentina).J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Apr 8;57(7):2691-8. doi: 10.1021/jf803866t. J Agric Food Chem. 2009. PMID: 19334753
-
Grouping, Spectrum-Effect Relationship and Antioxidant Compounds of Chinese Propolis from Different Regions Using Multivariate Analyses and Off-Line Anti-DPPH Assay.Molecules. 2020 Jul 16;25(14):3243. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143243. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32708723 Free PMC article.
-
From functional food to medicinal product: systematic approach in analysis of polyphenolics from propolis and wine.Nutr J. 2009 Jul 22;8:33. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-8-33. Nutr J. 2009. PMID: 19624827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and antioxidant activity of polyphenols derived from propolis.Molecules. 2013 Dec 20;19(1):78-101. doi: 10.3390/molecules19010078. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 24362627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Antioxidant Activity of Propolis Samples from Different Geographical Regions.Plants (Basel). 2022 Apr 29;11(9):1203. doi: 10.3390/plants11091203. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35567206 Free PMC article.
-
Propolis Stands out as a Multifaceted Natural Product: Meta-Analysis on Its Sources, Bioactivities, Applications, and Future Perspectives.Life (Basel). 2025 May 9;15(5):764. doi: 10.3390/life15050764. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antimicrobial Properties of Poplar and Aspen-Poplar Propolises and Their Active Components against Selected Microorganisms, including Helicobacter pylori.Pathogens. 2022 Jan 31;11(2):191. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020191. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35215134 Free PMC article.
-
Stability, Content of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Emulsions with Propolis Extracts during Simulated In Vitro Digestion.Foods. 2024 Mar 2;13(5):779. doi: 10.3390/foods13050779. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472892 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Geographical Origin on Poplar Propolis Composition and the Impact of Human Microbiota.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jun 11;17(6):768. doi: 10.3390/ph17060768. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bogdanov S. Propolis: Composition, Health, Medicine: A Review. Bee Prod. Sci. 2014;1:1–40.
-
- Bankova V., de Castro S., Marcucci M. Propolis: Recent advances in chemistry and plant origin. Apidologie. 2000;31:3–15. doi: 10.1051/apido:2000102. - DOI
-
- Fedotova V.V., Konovalov D.A. Propolis research in Russia. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2019;53:500–509. doi: 10.5530/ijper.53.4s.144. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous