The YAP/TEAD Axis as a New Therapeutic Target in Osteosarcoma: Effect of Verteporfin and CA3 on Primary Tumor Growth
- PMID: 33419295
- PMCID: PMC7766439
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12123847
The YAP/TEAD Axis as a New Therapeutic Target in Osteosarcoma: Effect of Verteporfin and CA3 on Primary Tumor Growth
Abstract
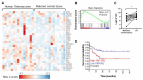
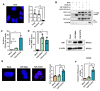
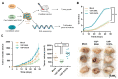
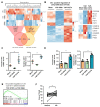
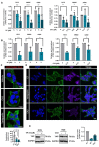
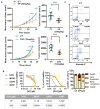
Although some studies suggested that disruption of the Hippo signaling pathway is associated with osteosarcoma progression, the molecular mechanisms by which YAP regulates primary tumor growth is not fully clarified. In addition, the validation of YAP as a therapeutic target through the use of inhibitors in a preclinical model must be demonstrated. RNA-seq analysis and Kaplan-Meier assays identified a YAP signature in osteosarcoma patients and a correlation with patients' outcomes. Molecular and cellular analysis (RNAseq, PLA, immunoprecipitation, promoter/specific gene, proliferation, cell cycle assays) using overexpression of mutated forms of YAP able or unable to interact with TEAD, indicate that TEAD is crucial for YAP-driven cell proliferation and in vivo tumor growth. In addition, in vivo experiments using an orthotopic mice model of osteosarcoma show that two YAP/TEAD inhibitors, verteporfin and CA3, reduce primary tumor growth. In this context, in vitro experiments demonstrate that these inhibitors decrease YAP expression, YAP/TEAD transcriptional activity and cell viability mainly by their ability to induce cell apoptosis. We thus demonstrate that the YAP/TEAD signaling axis is a central actor in mediating primary tumor growth of osteosarcoma, and that the use of YAP inhibitors may be a promising therapeutic strategy against osteosarcoma tumor growth.
Keywords: CA3; Hippo/YAP; osteosarcoma; tumor growth; verteporfin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of the TGF-β Signaling Pathway in the Development of YAP-Driven Osteosarcoma Lung Metastasis.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 26;11:765711. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.765711. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34765560 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK2 deprivation leads to the inhibition of tumor growth and metastatic potential in osteosarcoma cells through the modulation of YAP activity.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 26;38(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1506-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31878963 Free PMC article.
-
YAP-TEAD inhibition is associated with upregulation of an androgen receptor mediated transcription program providing therapeutic escape.FEBS Open Bio. 2024 Nov;14(11):1873-1887. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13901. Epub 2024 Sep 19. FEBS Open Bio. 2024. PMID: 39300603 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic molecules targeting yes associated protein activity as chemotherapeutics against cancer.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Dec;98(6):1025-1037. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13960. Epub 2021 Oct 3. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 34587361 Review.
-
Non-Photoinduced Biological Properties of Verteporfin.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(11):1171-84. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160316125048. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26980565 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of novel gene signatures for the risk stratification of prognosis and diagnostic prediction of osteosarcoma patients using bioinformatics analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Jul;11(7):2374-2387. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-1706. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35966307 Free PMC article.
-
Origin and Therapies of Osteosarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 19;14(14):3503. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143503. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the TGF-β Signaling Pathway in the Development of YAP-Driven Osteosarcoma Lung Metastasis.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 26;11:765711. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.765711. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34765560 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Hippo signaling in cancer: novel perspectives and therapeutic potential.MedComm (2020). 2023 Oct 3;4(5):e375. doi: 10.1002/mco2.375. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37799806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apelin promotes osteosarcoma metastasis by upregulating PLOD2 expression via the Hippo signaling pathway and hsa_circ_0000004/miR-1303 axis.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jan 1;19(2):412-425. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.77688. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36632453 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

