The Friction-Induced Vibration of Water-Lubricated Rubber Bearings during the Shutdown Process
- PMID: 33419332
- PMCID: PMC7767228
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13245818
The Friction-Induced Vibration of Water-Lubricated Rubber Bearings during the Shutdown Process
Abstract
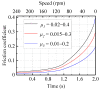
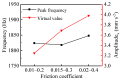
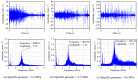
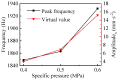
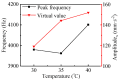
The vibration noise generated by water-lubricated rubber bearings (WLRBs) seriously reduces the concealment of a ship's navigation. The purpose of this study was to obtain the relationships between friction-induced vibration and the friction coefficient, specific pressure, temperature, and stiffness of the bearing support during the shutdown process of WLRBs. Using transient dynamic analysis (Abaqus/Standard), the shutdown process of the bearing system was simulated by setting a friction coefficient curve, and with the fast Fourier transform (FFT), the data in the time domain were then converted to the frequency domain. In addition, an orthogonal table was applied to select the best level for each factor. The results show that proportionally increasing the friction coefficient and specific pressure caused higher vibrations, and the effect of the specific pressure on vibration is more prominent than that of the friction coefficient. Higher temperatures led to an increase in the peak frequency of noise (squeal) and the virtual value of acceleration. Increasing the stiffness of the bearing support decreased the higher-frequency squeal but dramatically increased the lower-frequency chatter. The results of the study are of guiding significance for the improvement of research methods and the optimization of the materials and structures of WLRBs.
Keywords: friction-induced vibration; shutdown process; transient dynamics; tribology; water-lubricated rubber bearings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Bhushan B. Stick-Slip induced noise generation. J. Lubr. Technol. 1980;102:201–210. doi: 10.1115/1.3251470. - DOI
-
- Krauter A.I. Generation of squeal/chatter in water-lubricated elastomeric bearings. J. Tribol. 1981;103:406–412. doi: 10.1115/1.3251695. - DOI
-
- Simpson T.A., Ibrahim R.A. Nonlinear friction-induced vibration in water-lubricated bearings. JVC/J. Vib. Control. 1996;2:87–113. doi: 10.1177/107754639600200106. - DOI
-
- Hochlenert D. Nonlinear stability analysis of a disk brake model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2009;58:63–73. doi: 10.1007/s11071-008-9461-0. - DOI
-
- Hongling Q., Chang Y., Hefa Z., Xufei L., Zhixiong L., Xiang X. Experimental analysis on friction-induced vibration of water-lubricated bearings in a submarine propulsion system. Ocean Eng. 2020;203:107239. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107239. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

