Targeting mitochondrial ion channels for cancer therapy
- PMID: 33419703
- PMCID: PMC8113036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101846
Targeting mitochondrial ion channels for cancer therapy
Abstract
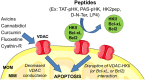
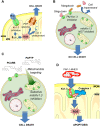
Pharmacological targeting of mitochondrial ion channels is emerging as a promising approach to eliminate cancer cells; as most of these channels are differentially expressed and/or regulated in cancer cells in comparison to healthy ones, this strategy may selectively eliminate the former. Perturbation of ion fluxes across the outer and inner membranes is linked to alterations of redox state, membrane potential and bioenergetic efficiency. This leads to indirect modulation of oxidative phosphorylation, which is/may be fundamental for both cancer and cancer stem cell survival. Furthermore, given the crucial contribution of mitochondria to intrinsic apoptosis, modulation of their ion channels leading to cytochrome c release may be of great advantage in case of resistance to drugs triggering apoptotic events upstream of the mitochondrial phase. In the present review, we give an overview of the known mitochondrial ion channels and of their modulators capable of killing cancer cells. In addition, we discuss state-of-the-art strategies using mitochondriotropic drugs or peptide-based approaches allowing a more efficient and selective targeting of mitochondrial ion channel-linked events.
Keywords: Cancer; Channel interactions; Drug targeting; Ion channels; Mitochondria.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Contribution of Mitochondrial Ion Channels to Cancer Development and Progression.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;53(S1):63-78. doi: 10.33594/000000198. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31860207 Review.
-
Small-Molecule Modulators of Mitochondrial Channels as Chemotherapeutic Agents.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;53(S1):11-43. doi: 10.33594/000000192. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31834993 Review.
-
The mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel 1 in tumor cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1848(10 Pt B):2547-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.10.040. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25448878 Review.
-
Mitochondrial ion channels as oncological targets.Oncogene. 2014 Dec 4;33(49):5569-81. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.578. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24469031 Review.
-
The role of the mitochondrial apoptosis induced channel MAC in cytochrome c release.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2005 Jun;37(3):155-64. doi: 10.1007/s10863-005-6570-z. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2005. PMID: 16167172 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Modulation of Ion Channels in Oncologic Symptomatology and Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 6;16(9):1786. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091786. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined activation of artificial and natural ion channels for disrupting mitochondrial ion homeostasis towards effective postoperative tumor recurrence and metastasis suppression.Theranostics. 2024 May 27;14(8):3282-3299. doi: 10.7150/thno.94855. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38855179 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Oxidative Phosphorylation on Cancer Drug Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;15(1):62. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010062. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Interplay between Dysregulated Ion Transport and Mitochondrial Architecture as a Dangerous Liaison in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 14;22(10):5209. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105209. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34069047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysical Mechanisms of Vaginal Smooth Muscle Contraction: The Role of the Membrane Potential and Ion Channels.Pathophysiology. 2024 May 14;31(2):225-243. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology31020018. Pathophysiology. 2024. PMID: 38804298 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

