Perceiving ensemble statistics of novel image sets
- PMID: 33420715
- PMCID: PMC8049939
- DOI: 10.3758/s13414-020-02174-0
Perceiving ensemble statistics of novel image sets
Abstract
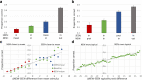
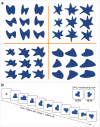
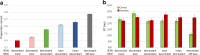
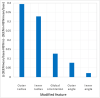
Perception, representation, and memory of ensemble statistics has attracted growing interest. Studies found that, at different abstraction levels, the brain represents similar items as unified percepts. We found that global ensemble perception is automatic and unconscious, affecting later perceptual judgments regarding individual member items. Implicit effects of set mean and range for low-level feature ensembles (size, orientation, brightness) were replicated for high-level category objects. This similarity suggests that analogous mechanisms underlie these extreme levels of abstraction. Here, we bridge the span between visual features and semantic object categories using the identical implicit perception experimental paradigm for intermediate novel visual-shape categories, constructing ensemble exemplars by introducing systematic variations of a central category base or ancestor. In five experiments, with different item variability, we test automatic representation of ensemble category characteristics and its effect on a subsequent memory task. Results show that observer representation of ensembles includes the group's central shape, category ancestor (progenitor), or group mean. Observers also easily reject memory of shapes belonging to different categories, i.e. originating from different ancestors. We conclude that complex categories, like simple visual form ensembles, are represented in terms of statistics including a central object, as well as category boundaries. We refer to the model proposed by Benna and Fusi (bioRxiv 624239, 2019) that memory representation is compressed when related elements are represented by identifying their ancestor and each one's difference from it. We suggest that ensemble mean perception, like category prototype extraction, might reflect employment at different representation levels of an essential, general representation mechanism.
Keywords: Categorization; Ensemble Perception; Implicit/explicit memory; Visual perception.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Comparing explicit and implicit ensemble perception: 3 stimulus variables and 3 presentation modes.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2024 Feb;86(2):482-502. doi: 10.3758/s13414-023-02784-4. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2024. PMID: 37821745 Free PMC article.
-
Relating categorization to set summary statistics perception.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2019 Nov;81(8):2850-2872. doi: 10.3758/s13414-019-01792-7. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2019. PMID: 31243687 Free PMC article.
-
Visual features as stepping stones toward semantics: Explaining object similarity in IT and perception with non-negative least squares.Neuropsychologia. 2016 Mar;83:201-226. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.10.023. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Neuropsychologia. 2016. PMID: 26493748 Free PMC article.
-
Ensemble Perception.Annu Rev Psychol. 2018 Jan 4;69:105-129. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010416-044232. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Annu Rev Psychol. 2018. PMID: 28892638 Review.
-
Hierarchies, similarity, and interactivity in object recognition: "category-specific" neuropsychological deficits.Behav Brain Sci. 2001 Jun;24(3):453-76; discussion 476-509. Behav Brain Sci. 2001. PMID: 11682799 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing explicit and implicit ensemble perception: 3 stimulus variables and 3 presentation modes.Atten Percept Psychophys. 2024 Feb;86(2):482-502. doi: 10.3758/s13414-023-02784-4. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2024. PMID: 37821745 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptual history biases in serial ensemble representation.J Vis. 2023 Mar 1;23(3):7. doi: 10.1167/jov.23.3.7. J Vis. 2023. PMID: 36920389 Free PMC article.
-
Ensemble percepts of colored targets among distractors are influenced by hue similarity, not categorical identity.J Vis. 2024 Oct 3;24(11):12. doi: 10.1167/jov.24.11.12. J Vis. 2024. PMID: 39412766 Free PMC article.
-
Neural representations of statistical and rule-based predictions in Gilles de la Tourette syndrome.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Jun 1;45(8):e26719. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26719. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38826009 Free PMC article.
-
The combination operation of grouping and ensemble coding for structured biological motion crowds in working memory.Cogn Res Princ Implic. 2024 Jul 10;9(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s41235-024-00574-6. Cogn Res Princ Implic. 2024. PMID: 38985366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allik J, Toom M, Raidvee A, Averin K, Kreegipuu K. Obligatory averaging in mean size perception. Vision Research. 2014;101:34–40. - PubMed
-
- Ariely D. Seeing sets: Representation by statistical properties. Psychological Science. 2001;12(2):157–162. - PubMed
-
- Ashby FG, Maddox WT. A response time theory of separability and integrality in speeded classification. Journal of Mathematical Psychology. 1994;38:423–466. doi: 10.1006/jmps.1994.1032. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

