The Use of Rifaximin in Patients With Cirrhosis
- PMID: 33421158
- PMCID: PMC8518409
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.31708
The Use of Rifaximin in Patients With Cirrhosis
Abstract
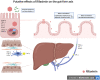
Rifaximin is an oral nonsystemic antibiotic with minimal gastrointestinal absorption and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity covering both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. Rifaximin is currently used worldwide in patients with cirrhosis for preventing recurrent HE because its efficacy and safety have been proven by large randomized clinical trials. In the last decade, experimental and clinical evidence suggest that rifaximin could have other beneficial effects on the course of cirrhosis by modulating the gut microbiome and affecting the gut-liver axis, which in turn can interfere with major events of the pathophysiological cascade underlying decompensated cirrhosis, such as systemic inflammatory syndrome, portal hypertension, and bacterial infections. However, the use of rifaximin for prevention or treatment of other complications, including spontaneous bacterial peritonitis or other bacterial infections, is not accepted because evidence by clinical trials is still very weak. The present review deals in the first part with the potential impact of rifaximin on pathogenic mechanisms in liver diseases, whereas in the second part, its clinical effects are critically discussed. It clearly emerges that, because of its potential activity on multiple pathogenic events, the efficacy of rifaximin in the prevention or management of complications other than HE deserves to be investigated extensively. The results of double-blinded, adequately powered randomized clinical trials assessing the effect of rifaximin, alone or in combination with other drugs, on hard clinical endpoints, such as decompensation of cirrhosis, acute-on-chronic liver failure, and mortality, are therefore eagerly awaited.
© 2021 The Authors. Hepatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Macbeth WA, Kass EH, McDermott WV Jr. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by alteration of intestinal flora with lactobacillus acidophilus. Lancet 1965;1:399‐403. - PubMed
-
- Riordan SM, Williams R. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 1997;337:473‐479. - PubMed
-
- Conn HO, Leevy CM, Vlahcevic ZR, Rodgers JB, Maddrey WC, Seeff L, et al. Comparison of lactulose and neomycin in the treatment of chronic portal‐systemic encephalopathy. A double‐blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology 1977;72:573‐583. - PubMed
-
- Bass NM, Mullen KD, Sanyal A, Poordad F, Neff G, Leevy CB, et al. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1071‐1081. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj JS, Khoruts A. Microbiota changes and intestinal microbiota transplantation in liver diseases and cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2020;72:1003‐1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

