Systemic Treatment of Advanced Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in Korea: Literature Review and Expert Opinion
- PMID: 33421978
- PMCID: PMC8053871
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2020.1233
Systemic Treatment of Advanced Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in Korea: Literature Review and Expert Opinion
Abstract
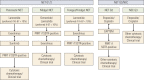
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a group of malignancies arising from neuroendocrine cells and frequently originate in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas. Although curative resection is the main treatment for localized disease, systemic therapy is needed for relapsed or metastatic/unresectable gastroenteropancreatic NETs (GEP-NETs). Although there are several NET treatment guidelines from various countries, the geographical discrepancies between patient clinical characteristics, the regulatory approval status for therapeutic agents, and medical practices necessitate specific guidelines for Korean patients. We here provide a consensus review of the diagnosis, staging and systemic treatment of Korean GEP-NET patients. Systemic therapy options and the current Korean expert consensus on these treatments, including somatostatin analogs, targeted therapies such as everolimus and sunitinib, peptide receptor radionuclide treatments, and cytotoxic chemotherapies are addressed.
Keywords: Capecitabine; Everolimus; Lanreotide; Neuroendocrine tumor; Octreotide; Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy; Sunitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
CY has received research grants and honoraria from Ipsen and honoraria from Novartis. S-TK, WKB, H-JC, M-AL, and B-YR have received honoraria from Ipsen.
Figures
References
-
- Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, Dagohoy C, Leary C, Mares JE, et al. One hundred years after “carcinoid”: epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3063–72. - PubMed
-
- Frilling A, Modlin IM, Kidd M, Russell C, Breitenstein S, Salem R, et al. Recommendations for management of patients with neuroendocrine liver metastases. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e8–21. - PubMed
-
- Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of Korean Society of Pathologists. Cho MY, Kim JM, Sohn JH, Kim MJ, Kim KM, et al. Current trends of the incidence and pathological diagnosis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs) in Korea 2000–2009: multicenter study. Cancer Res Treat. 2012;44:157–65. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical