The rocaglate CR-31-B (-) inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication at non-cytotoxic, low nanomolar concentrations in vitro and ex vivo
- PMID: 33422611
- PMCID: PMC7791309
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105012
The rocaglate CR-31-B (-) inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication at non-cytotoxic, low nanomolar concentrations in vitro and ex vivo
Abstract
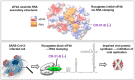
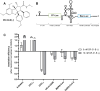
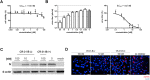
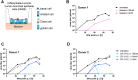
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative agent of COVID-19, a severe respiratory disease with varying clinical presentations and outcomes, and responsible for a major pandemic that started in early 2020. With no vaccines or effective antiviral treatments available, the quest for novel therapeutic solutions remains an urgent priority. Rocaglates, a class of plant-derived cyclopenta[b]benzofurans, exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activity against multiple RNA viruses including coronaviruses. Specifically, rocaglates inhibit eukaryotic initiation factor 4A (eIF4A)-dependent mRNA translation initiation, resulting in strongly reduced viral RNA translation. Here, we assessed the antiviral activity of the synthetic rocaglate CR-31-B (-) against SARS-CoV-2 using both in vitro and ex vivo cell culture models. In Vero E6 cells, CR-31-B (-) inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication with an EC50 of ~1.8 nM. In primary human airway epithelial cells, CR-31-B (-) reduced viral titers to undetectable levels at a concentration of 100 nM. Reduced virus reproduction was accompanied by substantially reduced viral protein accumulation and replication/transcription complex formation. The data reveal a potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity by CR-31-B (-), corroborating previous results obtained for other coronaviruses and supporting the idea that rocaglates may be used in first-line antiviral intervention strategies against novel and emerging RNA virus outbreaks.
Keywords: Antiviral activity; COVID-19; Rocaglate; SARS-CoV-2; Translation initiation; eIF4A.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amidino-rocaglates (ADRs), a class of synthetic rocaglates, are potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 replication through inhibition of viral protein synthesis.Antiviral Res. 2024 Oct;230:105976. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105976. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 39117283
-
Comparison of broad-spectrum antiviral activities of the synthetic rocaglate CR-31-B (-) and the eIF4A-inhibitor Silvestrol.Antiviral Res. 2020 Mar;175:104706. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104706. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 31931103 Free PMC article.
-
Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity of 3D8, a Nucleic Acid-Hydrolyzing Single-Chain Variable Fragment (scFv), Targeting SARS-CoV-2 and Multiple Coronaviruses In Vitro.Viruses. 2021 Apr 9;13(4):650. doi: 10.3390/v13040650. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33918914 Free PMC article.
-
Flavaglines as natural products targeting eIF4A and prohibitins: From traditional Chinese medicine to antiviral activity against coronaviruses.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 1;203:112653. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112653. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32693294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structures and functions of coronavirus replication-transcription complexes and their relevance for SARS-CoV-2 drug design.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Jan;23(1):21-39. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00432-z. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34824452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of structurally re-engineered rocaglates as inhibitors against hepatitis E virus replication.Antiviral Res. 2022 Aug;204:105359. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105359. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Antiviral Res. 2022. PMID: 35728703 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Discovery of a Therapeutic Lead for HFMD From a Library Screen of Rocaglates/Aglains.J Med Virol. 2025 Feb;97(2):e70228. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70228. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 39921602 Free PMC article.
-
Amidino-rocaglates (ADRs), a class of synthetic rocaglates, are potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 replication through inhibition of viral protein synthesis.Antiviral Res. 2024 Oct;230:105976. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105976. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 39117283
-
Platelet Phenotype Analysis of COVID-19 Patients Reveals Progressive Changes in the Activation of Integrin αIIbβ3, F13A1, the SARS-CoV-2 Target EIF4A1 and Annexin A5.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 11;8:779073. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.779073. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34859078 Free PMC article.
-
Some natural compounds and their analogues having potent anti- SARS-CoV-2 and anti-proteases activities as lead molecules in drug discovery for COVID-19.Eur J Med Chem Rep. 2022 Dec;6:100079. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmcr.2022.100079. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Eur J Med Chem Rep. 2022. PMID: 36060987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams T.E., El Sous M., Hawkins B.C., et al. Total synthesis of the potent anticancer Aglaia metabolites (-)-silvestrol and (-)-episilvestrol and the actice analogue (-)-4'-desmethoxyepisilvestrol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:1607–1616. - PubMed
-
- Biedenkopf N., Lange-Grünweller K., Schulte F.W., et al. The natural compound silvestrol is a potent inhibitor of Ebola virus replication. Antivir. Res. 2017;137:76–81. - PubMed
-
- Bronstrup M., Sasse F. Natural products targeting the elongation phase of eukaryotic protein biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020;37:752–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

