Transfer learning for predicting conversion from mild cognitive impairment to dementia of Alzheimer's type based on a three-dimensional convolutional neural network
- PMID: 33422894
- PMCID: PMC7902477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.12.005
Transfer learning for predicting conversion from mild cognitive impairment to dementia of Alzheimer's type based on a three-dimensional convolutional neural network
Abstract
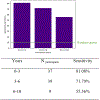
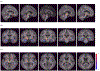
Dementia of Alzheimer's type (DAT) is associated with devastating and irreversible cognitive decline. Predicting which patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) will progress to DAT is an ongoing challenge in the field. We developed a deep learning model to predict conversion from MCI to DAT. Structural magnetic resonance imaging scans were used as input to a 3-dimensional convolutional neural network. The 3-dimensional convolutional neural network was trained using transfer learning; in the source task, normal control and DAT scans were used to pretrain the model. This pretrained model was then retrained on the target task of classifying which MCI patients converted to DAT. Our model resulted in 82.4% classification accuracy at the target task, outperforming current models in the field. Next, we visualized brain regions that significantly contribute to the prediction of MCI conversion using an occlusion map approach. Contributory regions included the pons, amygdala, and hippocampus. Finally, we showed that the model's prediction value is significantly correlated with rates of change in clinical assessment scores, indicating that the model is able to predict an individual patient's future cognitive decline. This information, in conjunction with the identified anatomical features, will aid in building a personalized therapeutic strategy for individuals with MCI.
Keywords: Convolutional neural network; Dementia of Alzheimer's type; Magnetic resonance imaging; Mild cognitive impairment; Predictive modeling.
Crown Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Statement
This manuscript has nothing to disclose for actual or potential conflict and interest.
Figures
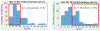

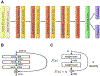


References
-
- Alzheimer's Association. 2019 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 2019;15(3):321–87.
-
- Ardila D, Kiraly AP, Bharadwaj S, Choi B, Reicher JJ, Peng L, Tse D, Etemadi M, Ye W, Corrado G End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat Med 2019;25(6):954–61. - PubMed
-
- Ball M, Hachinski V, Fox A, Kirshen A, Fisman M, Blume W, Kral V, Fox H, Merskey H. A new definition of Alzheimer's disease: a hippocampal dementia. Lancet 1985;325(8419):14–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

