A supernumerary designer chromosome for modular in vivo pathway assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 33423048
- PMCID: PMC7897487
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1167
A supernumerary designer chromosome for modular in vivo pathway assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
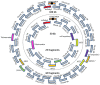
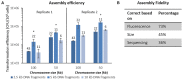
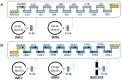
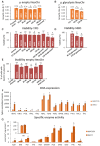
The construction of microbial cell factories for sustainable production of chemicals and pharmaceuticals requires extensive genome engineering. Using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, this study proposes synthetic neochromosomes as orthogonal expression platforms for rewiring native cellular processes and implementing new functionalities. Capitalizing the powerful homologous recombination capability of S. cerevisiae, modular neochromosomes of 50 and 100 kb were fully assembled de novo from up to 44 transcriptional-unit-sized fragments in a single transformation. These assemblies were remarkably efficient and faithful to their in silico design. Neochromosomes made of non-coding DNA were stably replicated and segregated irrespective of their size without affecting the physiology of their host. These non-coding neochromosomes were successfully used as landing pad and as exclusive expression platform for the essential glycolytic pathway. This work pushes the limit of DNA assembly in S. cerevisiae and paves the way for de novo designer chromosomes as modular genome engineering platforms in S. cerevisiae.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modular, synthetic chromosomes as new tools for large scale engineering of metabolism.Metab Eng. 2022 Jul;72:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2021.12.013. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Metab Eng. 2022. PMID: 35051627
-
One-step assembly and targeted integration of multigene constructs assisted by the I-SceI meganuclease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Yeast Res. 2013 Dec;13(8):769-81. doi: 10.1111/1567-1364.12087. Epub 2013 Oct 7. FEMS Yeast Res. 2013. PMID: 24028550 Free PMC article.
-
A versatile, efficient strategy for assembly of multi-fragment expression vectors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using 60 bp synthetic recombination sequences.Microb Cell Fact. 2013 May 10;12:47. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-47. Microb Cell Fact. 2013. PMID: 23663359 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in systems and synthetic biology approaches for developing novel cell-factories in non-conventional yeasts.Biotechnol Adv. 2021 Mar-Apr;47:107695. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107695. Epub 2021 Jan 16. Biotechnol Adv. 2021. PMID: 33465474 Review.
-
Efficient assembly of a synthetic attenuated SARS-CoV-2 genome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using multi-copy yeast vectors.J Genet. 2024;103:09. J Genet. 2024. PMID: 38379228 Review.
Cited by
-
Application and Technical Challenges in Design, Cloning, and Transfer of Large DNA.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;10(12):1425. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10121425. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A supernumerary synthetic chromosome in Komagataella phaffii as a repository for extraneous genetic material.Microb Cell Fact. 2023 Dec 16;22(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02262-4. Microb Cell Fact. 2023. PMID: 38104077 Free PMC article.
-
Convenient synthesis and delivery of a megabase-scale designer accessory chromosome empower biosynthetic capacity.Cell Res. 2024 Apr;34(4):309-322. doi: 10.1038/s41422-024-00934-3. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38332200 Free PMC article.
-
Top-Down, Knowledge-Based Genetic Reduction of Yeast Central Carbon Metabolism.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0297021. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02970-21. Epub 2022 Sep 21. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36129294 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Genomics From a Yeast Perspective.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 21;10:869486. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.869486. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35387293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Walker G.M., Walker R.S.K.. Gadd G.M., Sariaslani S.. Chapter three - Enhancing yeast alcoholic fermentations. Advances in Applied Microbiology. 2018; 105:Academic Press; 87–129. - PubMed
-
- Meehl M.A., Stadheim T.A.. Biopharmaceutical discovery and production in yeast. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014; 30:120–127. - PubMed
-
- Paddon C.J., Keasling J.D.. Semi-synthetic artemisinin: a model for the use of synthetic biology in pharmaceutical development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014; 12:355–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

