Human liver model systems in a dish
- PMID: 33423319
- PMCID: PMC7940568
- DOI: 10.1111/dgd.12708
Human liver model systems in a dish
Abstract
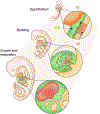
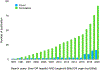
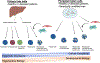
The human adult liver has a multi-cellular structure consisting of large lobes subdivided into lobules containing portal triads and hepatic cords lined by specialized blood vessels. Vital hepatic functions include filtering blood, metabolizing drugs, and production of bile and blood plasma proteins like albumin, among many other functions, which are generally dependent on the location or zone in which the hepatocyte resides in the liver. Due to the liver's intricate structure, there are many challenges to design differentiation protocols to generate more mature functional hepatocytes from human stem cells and maintain the long-term viability and functionality of primary hepatocytes. To this end, recent advancements in three-dimensional (3D) stem cell culture have accelerated the generation of a human miniature liver system, also known as liver organoids, with polarized epithelial cells, supportive cell types and extra-cellular matrix deposition by translating knowledge gained in studies of animal organogenesis and regeneration. To facilitate the efforts to study human development and disease using in vitro hepatic models, a thorough understanding of state-of-art protocols and underlying rationales is essential. Here, we review rapidly evolving 3D liver models, mainly focusing on organoid models differentiated from human cells.
Keywords: liver; organogenesis; organoid; regeneration; stem cell.
© 2021 Japanese Society of Developmental Biologists.
Figures

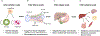
References
-
- Ardalani H, Sengupta S, Harms V, Vickerman V, Thomson JA, and Murphy WL (2019). 3-D Culture and Endothelial Cells Improve Maturity of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocytes. Acta Biomaterialia 95, 371–381. - PubMed
-
- Bell CC, Hendriks DFG, Moro SML, Ellis E, Walsh J, Renblom A, Fredriksson Puigvert L, Dankers ACA, Jacobs F, Snoeys J, et al. (2016). Characterization of primary human hepatocyte spheroids as a model system for drug-induced liver injury, liver function and disease. Scientific Reports 6, 25187. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bell CC, Lauschke VM, Vorrink SU, Palmgren H, Duffin R, Andersson TB, and Ingelman-Sundberg M (2017). Transcriptional, Functional, and Mechanistic Comparisons of Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocytes, HepaRG Cells, and Three-Dimensional Human Hepatocyte Spheroids as Predictive In Vitro Systems for Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Drug Metab Dispos 45, 419–429. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger DR, Ware BR, Davidson MD, Allsup SR, and Khetani SR (2015). Enhancing the functional maturity of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived human hepatocytes by controlled presentation of cell-cell interactions in vitro. Hepatology 61, 1370–1381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

