Hypoxia, endoplasmic reticulum stress and chemoresistance: dangerous liaisons
- PMID: 33423689
- PMCID: PMC7798239
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-020-01824-3
Hypoxia, endoplasmic reticulum stress and chemoresistance: dangerous liaisons
Abstract
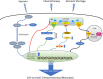
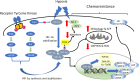
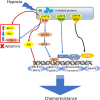
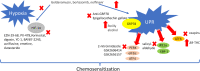
Solid tumors often grow in a micro-environment characterized by < 2% O2 tension. This condition, together with the aberrant activation of specific oncogenic patwhays, increases the amount and activity of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), a transcription factor that controls up to 200 genes involved in neoangiogenesis, metabolic rewiring, invasion and drug resistance. Hypoxia also induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, a condition that triggers cell death, if cells are irreversibly damaged, or cell survival, if the stress is mild.Hypoxia and chronic ER stress both induce chemoresistance. In this review we discuss the multiple and interconnected circuitries that link hypoxic environment, chronic ER stress and chemoresistance. We suggest that hypoxia and ER stress train and select the cells more adapted to survive in unfavorable conditions, by activating pleiotropic mechanisms including apoptosis inhibition, metabolic rewiring, anti-oxidant defences, drugs efflux. This adaptative process unequivocally expands clones that acquire resistance to chemotherapy.We believe that pharmacological inhibitors of HIF-1α and modulators of ER stress, although characterized by low specificty and anti-cancer efficacy when used as single agents, may be repurposed as chemosensitizers against hypoxic and chemorefractory tumors in the next future.
Keywords: Chemoresistance; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Hypoxia; Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; Unfolded protein response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Finley LWS, Thompson CB, Mendelsohn J, Gray JW, Howley PM, Israel MA. 13 - The Metabolism of Cell Growth and Proliferation. The Molecular Basis of Cancer (Fourth Edition). Philadelphia: Content Repository Only; 2015. p. 191–208.e2.
-
- Ivanovic Z, Vlaski-Lafarge M. 2 - In Situ Normoxia versus “Hypoxia”. Anaerobiosis and Stemness. Boston: Academic Press; 2016. pp. 17–21.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

